As electronic devices continue to push the boundaries of speed, performance, and miniaturization, the need for more reliable, heat-resistant materials has skyrocketed. Enter the TG180 PCB, a versatile and durable solution built for environments that would melt lesser boards. In industries ranging from aerospace to automotive, TG180 PCBs are proving themselves to be the sturdy workhorses that engineers and manufacturers trust when the heat is on—literally.
But what sets TG180 PCBs apart from other materials, such as TG150 or TG140? In this deep dive, we’ll break down the technical advantages, best design practices, and use cases for TG180 PCBs, helping you understand why this material is becoming a go-to in the world of high-performance electronics.
The Unique Temperature Effects on TG180 PCB
TG180 PCBs provide remarkable thermal stability, but the impact of temperature on their dielectric constant (Dk) and mechanical properties is worth exploring for optimal performance.
How Elevated Temperatures Impact Dielectric Constant (Dk) and Signal Integrity?
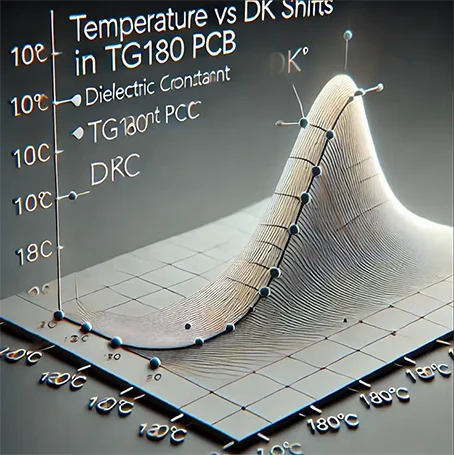
Temperature shifts, especially in high-performance PCBs, can affect the dielectric constant (Dk), which influences the signal transmission quality. As temperatures rise, TG180 materials experience minimal shifts in Dk, helping to preserve signal integrity, particularly in high-speed designs.
Signal Transmission at High Frequencies
For boards operating at high frequencies, maintaining stable Dk is crucial. TG180’s material properties ensure that signal degradation is minimized, providing consistent performance across a range of frequencies. By optimizing trace routing and ensuring proper impedance matching, designers can take full advantage of TG180’s stability.
Here’s a graphical representation of how temperature impacts the dielectric constant (Dk) for TG180 material:
Impact on Communication Systems
In telecommunication systems or network infrastructures, where maintaining signal clarity at high frequencies is key, TG180 boards offer the reliability needed in environments with fluctuating temperatures.
Thermal Expansion and Mechanical Stress on TG180 Boards
While TG180 PCBs perform well under thermal stress, like any material, they are subject to expansion when exposed to high temperatures. However, their superior mechanical stability means they can handle thermal expansion better than lower-grade materials.
Mitigating Thermal Expansion with Optimized Layouts
To mitigate the effects of thermal expansion, designers should adopt techniques such as:
● Thermal relief pads around vias.
● Balanced copper pours to distribute heat evenly.
● Placing thermal vias under heat-generating components to manage temperature distribution.
Long-Term Effects of High-Temperature Exposure
When continuously exposed to temperatures nearing 180°C, lower-grade materials may warp or delaminate. TG180’s high Tg protects the board from such effects, but it’s always good practice to incorporate cooling techniques like heat sinks or fans to ensure longevity.
The Role of Thermal Management in TG180 PCBs
As performance demands increase, so do the thermal challenges in PCBs. With TG180 boards, it’s essential to design with heat dissipation in mind, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the board.
Implementing Heat Sinks for Heat Management
Heat sinks are crucial in pulling heat away from high-power components. By pairing TG180 boards with appropriate heat sinks, designers can ensure that the system remains cool even when subjected to continuous operation.
The Importance of Thermal Vias
Thermal vias offer an effective solution to dissipate heat through the layers of the PCB. This technique spreads the heat more evenly, preventing hotspots and reducing overall thermal stress on the board.
TG180 vs. TG150 vs. TG140: A Deep Dive into Material Properties
When it comes to high-Tg PCBs, it’s essential to understand the unique characteristics that make TG180 stand out from its siblings, TG150 and TG140. These materials differ not just in their temperature ratings but also in how they handle heat dissipation, mechanical stress, and signal integrity.
Key Material Properties of TG180
TG180 refers to the glass transition temperature of 180°C, meaning the PCB material can withstand continuous operation at this temperature without degrading. However, that’s just scratching the surface. TG180 excels in several key performance areas, including:
1)Thermal Conductivity: TG180 materials typically exhibit superior heat dissipation, a crucial factor for high-speed applications where power consumption generates significant thermal loads.
2)Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): The CTE of TG180 materials is lower compared to TG150 and TG140, making it better suited for high-density interconnect (HDI) designs where mechanical stress can cause warping or misalignment.
| Property | TG140 | TG150 | TG180 |
| Glass Transition (Tg) | 140°C | 150°C | 180°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | Medium | Medium | High |
| CTE | High | Medium | Low |
| Moisture Absorption | Medium | Low | Low |
Ready to future-proof your next big project? With 5G, EVs, and AI pushing the boundaries of what electronics can do, TG180 is your go-to material for handling the heat—literally and figuratively. Whether you’re designing for telecom, automotive, or aerospace, this is one investment you won’t regret.
TG180 vs. TG150 and TG140: Application Differences
●TG140 is typically found in consumer electronics where heat dissipation isn’t a primary concern.
●TG150 takes a step up, being a better choice for industrial applications like power supplies.
●TG180, however, shines in automotive and aerospace applications, where constant high temperatures require both stability and reliability.
Cost vs. Performance Balance
Yeah, TG180 might have a bit more sticker shock compared to TG150 and TG140, but let’s be real—it’s like buying quality work boots. Sure, you’ll drop more cash upfront, but the durability and fewer replacements down the line more than make up for it. With TG180, you’re investing in performance that’ll keep ticking when others would’ve bit the dust.
Real-World Case Study: TG180 in Electric Vehicles
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) market, heat dissipation is critical, especially in components like battery management systems (BMS) and motor control units. A major manufacturer recently adopted TG180 PCBs for their latest line of EVs, specifically to solve issues related to thermal cycling and power density. After switching to TG180, the company reported:
● A 25% reduction in thermal-related failures.
● Improved lifespan of critical components by up to 50%.
● Increased power throughput without additional cooling requirements.
Therefore, TG180 PCBs aren’t just riding the wave of popularity for no reason. Picture this: high-end automotive systems, like engine control units (ECUs), rely heavily on the robustness of TG180 materials to stay cool when things get heated under the hood. And it’s not just cars—telecom giants are all over TG180 for 5G infrastructure, making sure your Zoom calls don’t crash mid-sentence. The aerospace world also demands nothing less, where failure is simply not an option.
Best Design Practices for TG180 PCBs
Signal Integrity and High-Speed Design
Designing with TG180 materials presents unique opportunities—and challenges—especially in high-speed applications. As frequencies climb and component sizes shrink, maintaining signal integrity becomes more complex. Fortunately, TG180’s low dielectric constant (Dk) and loss tangent (Df) help minimize signal attenuation, but only if proper design practices are followed.
Impedance Matching and Crosstalk Suppression
For high-frequency designs, impedance matching is essential to avoid signal reflections. TG180 PCBs, with their low CTE and stable Dk, provide a good platform for maintaining consistent impedance across high-speed traces. However, designers must also account for:
1)Layer Stackup: A carefully considered stackup is vital. Aim for thin dielectric layers between signal layers to reduce loop inductance and improve signal integrity.
2)Crosstalk Mitigation: Employ techniques like ground planes and adequate trace spacing to minimize crosstalk. TG180’s thermal properties ensure that these structures remain stable under heat stress.
Thermal Management with TG180 PCBs
If you think slapping a TG180 PCB into a high-temp environment is enough, think again, my friend. To really get the most out of this bad boy, you’ve got to combine it with solid thermal management. We’re talking heat sinks, thermal vias, and smart board layouts that keep things cool under pressure. Picture it like setting up fans at a summer barbecue—you gotta direct that heat out, or things are gonna sizzle for all the wrong reasons.
So, when dealing with high-power applications, effective thermal management is crucial. TG180 materials, thanks to their excellent thermal conductivity, allow for more aggressive thermal designs without the risk of board degradation.
Best Practices for Thermal Dissipation
● Use Copper Pour: A copper pour on power and ground layers can enhance heat dissipation.
● Vias for Heat Dissipation: Place thermal vias strategically under heat-generating components to help direct heat away from critical areas.
●Heat Sinks and Pads: Use external heat sinks or thermal pads to dissipate excess heat, especially in areas with concentrated power.
Environmental Impact and Compliance
You want your products out in the world, not stuck in the lab over compliance issues. TG180 PCBs make life a whole lot easier when it comes to ticking all the boxes—RoHS, UL 94V-0, and IPC standards. They’re like your reliable co-pilot, helping you navigate through all those certification hoops.
Durability in Harsh Environments
When it comes to TG180, we’re talking a serious workhorse. Think of it like that pickup truck that refuses to quit, even when the road gets rough. TG180 PCBs handle not just high heat but extreme environments where humidity and vibrations could make other materials tap out early. This makes them perfect for military applications and heavy-duty industrial systems, where longevity and reliability are the name of the game.
RoHS and REACH Compliance
As industries move toward greener manufacturing processes, PCB materials like TG180 are helping companies stay compliant with stringent regulations like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals). TG180 PCBs are typically lead-free, making them an excellent choice for manufacturers aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
1)Lead-Free Soldering: TG180 PCBs are compatible with lead-free soldering processes, reducing toxic waste and contributing to cleaner production methods.
2)Lower Carbon Footprint: By offering a longer lifespan in high-temperature applications, TG180 reduces the need for frequent replacements, thus lowering the overall environmental impact.
The Future of Eco-Friendly Electronics
With increasing attention on sustainability, TG180 PCBs are expected to play a vital role in the development of eco-friendly electronics. Manufacturers are already experimenting with recyclable materials and energy-efficient production processes to further reduce the environmental footprint of high-Tg PCBs.
Advanced Design Tools for TG180 PCBs
If you’re thinking about winging it with TG180, you might wanna pump the brakes. Advanced simulation tools like ANSYS or Altium Designer are your best pals when it comes to making sure thermal and signal integrity hold steady. These tools are like test-driving a car before you buy—you get to see how everything’s gonna handle before committing.
Therefore, to fully leverage the potential of TG180 materials, design engineers often turn to advanced simulation tools. These tools not only optimize thermal and mechanical performance but also ensure signal integrity in complex designs.
Simulation Tools for High-Performance PCB Design
1)Ansys HFSS: Ideal for high-frequency simulations, allowing engineers to optimize trace width, spacing, and stackup for signal integrity.
2)Thermal Simulation Tools: Use tools like Mentor Graphics FloTHERM to simulate thermal behavior in real-time, identifying hotspots and optimizing via placement.
Are you ready to elevate your designs with the robust performance of TG180 PCBs? Whether you’re an engineer grappling with heat management or a procurement professional looking for long-lasting, eco-friendly solutions, TG180 is the material that delivers—time and again.
Explore detailed design resources, stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends, and contact a TG180 PCB manufacturer-JarnisTech to discuss how this high-performance material can be customized to meet your unique needs.
Wrapping Up
Why TG180 Should Be Your Next PCB Material?
If you’re working on high-performance electronics where heat is a constant challenge, TG180 PCBs are the way to go. With superior thermal stability, mechanical strength, and compatibility with modern soldering techniques, these boards offer the reliability and performance needed for the most demanding applications.
With its unmatched thermal stability, superior signal integrity, and eco-friendly credentials, TG180 is becoming the material of choice for high-performance applications. As industries continue to demand more from their electronics, TG180 PCBs offer the reliability and durability to stay ahead of the curve. Whether you’re designing for automotive, aerospace, or high-speed communication, TG180 has you covered.
Frequently Asked Questions About TG180 PCBs
A: What are the main benefits of TG180 PCBs?
Q: TG180 PCBs offer superior heat resistance, mechanical strength, and reliability, making them ideal for high-temperature and high-power applications.
A: Can TG180 PCBs be used in consumer electronics?
Q: While TG180 can be used in consumer electronics, it’s overkill for most low-power devices. TG180 is better suited for industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications where temperature and stress are key factors.
A: What industries typically use TG180 PCBs?
Q: Automotive, aerospace, industrial control systems, and power electronics are the primary industries that rely on TG180 PCBs.