The performance of substrate material is a critical factor that significantly influences the fundamental attributes of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). PCB manufacturers understand that in order to enhance the performance of circuit boards, they must first optimize the substrate material’s performance. In response to the demand for compatibility with market trends and new technologies, numerous novel substrate materials have been developed and are currently being integrated into PCB applications.
In recent years, the focus within the PCB market has shifted from traditional hardware products like desktop PCs to wireless communication devices such as servers and mobile terminals. Smartphones, in particular, have played a significant role in driving PCB development towards high-density, lightweight, and multi-functional designs.
It should be noted that the technological demands of substrate material closely relate to the performance of PCBs, and as such, substrate material selection is critical in ensuring the quality and reliability of both the circuit boards and the end products they serve. Without advanced substrate materials, achieving optimal printed circuit technology is simply impossible.
What Is PCB Substrates?
PCB substrates, also known as printed circuit board substrates, are the base materials on which electronic components are mounted and connected to each other. The substrate is a non-conductive material used to provide mechanical support and insulation for the conductive components of the PCB. The choice of substrate material is critical, as it affects the electrical and mechanical properties of the finished PCB. Different substrate materials have different electrical properties, such as dielectric constant and thermal conductivity, and also affect the performance, reliability and cost of the finished PCB.
Types of PCB Substrates
There are several types of PCB substrates available in the market. Some of the most popular types are:
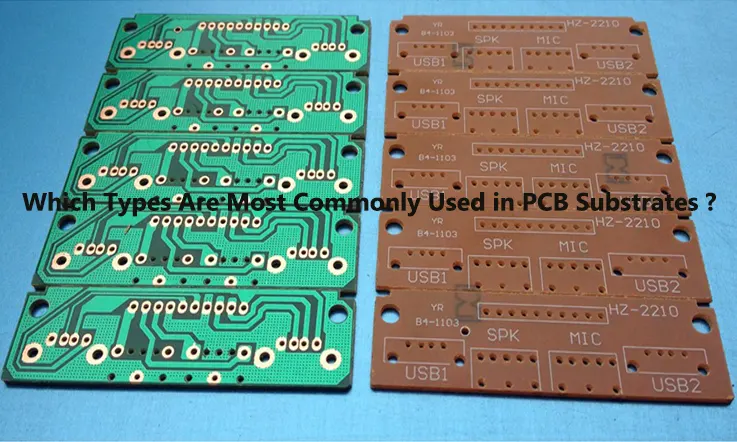
FR-4 Substrate
FR4 is a widely used substrate material in the production of printed circuit boards due to its cost-effectiveness, excellent electrical properties, and high mechanical strength. It consists of a composite of fiberglass and epoxy resin, providing it with outstanding electrical insulation properties and mechanical rigidity.
The acronym “FR4” denotes “Flame Retardant 4,” signifying its classification in the NEMA grade system. This system categorizes insulating materials used in the electronics industry based on their thermal and electrical properties. FR4 is commonly used as a laminate material for PCB substrate due to its superior performance characteristics.
Advantages of Using FR4 Substrates in PCB Manufacturing
● FR4 is a highly utilized substrate material in the PCB industry due to its wide availability, which translates to cost-effectiveness. Additionally, it exhibits good electrical insulation properties by virtue of its high dielectric constant, rendering it an excellent choice for electrical insulators.
● What’s more, the presence of fiberglass reinforcement in FR4 imparts it with remarkable mechanical strength, thus making it a suitable option for high-stress applications. It should be noted that FR4 has a relatively low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that enables it to remain stable under changing temperatures.
● Notably, FR4 enjoys broad application across diverse electronic sectors, from consumer electronics to industrial control systems. Moreover, it is frequently employed in the production of single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer PCBs.
Rogers Substrates
Rogers PCB substrates material is a type of rigid substrate utilized in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards. It is composed of a blend of polymer and ceramic materials, resulting in distinctive electrical and thermal characteristics unmatched by other PCB substrate materials.
Advantages of Using Rogers Substrates in PCB Manufacturing
● Rogers PCB material boasts a noteworthy range of properties that make it a prime choice for high-performance applications in the field of electronics. Its thermal stability is unparalleled, as the material possesses a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which ensures long-lasting dimensional integrity even under varying temperature conditions.
● Additionally, its superior electrical conductivity is characterized by a low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, making it an ideal material for high-frequency applications. The material’s high thermal conductivity amplifies its efficiency in promptly dispersing heat generated by electronic components during operation.
● Moreover, its composition of both polymer and ceramic components strengthens its mechanical stability, making it a preferred choice for high-stress applications.
These significant advantages make Rogers PCB material an exceptional choice for various high-frequency and high-performance electronic applications such as microwave and millimeter wave circuits, recognized for its consistent quality and reliability.
Metal-core Substrates
Metal-core PCBs, also known as MCPCBs, are a specialized type of printed circuit board that utilize a metallic substrate, typically composed of aluminum or copper, instead of standard insulating materials such as plastic or fiberglass. This unique construction allows for superior thermal conductivity compared to conventional PCBs, thereby making MCPCBs an optimal choice for use in high-heat applications including power electronics and high-power LED lighting. With improved thermal performance, MCPCBs can withstand thermal stress, ensuring consistent and reliable operation.
Advantages of Using Metal Core Substrates in PCB Manufacturing
● Metal-core PCBs offer enhanced thermal management and mechanical stability compared to traditional printed circuit boards. The metallic substrate of MCPCBs allows for improved heat dissipation, reducing the likelihood of thermal damage to electronics.
● Additionally, metal-core PCBs can operate at higher temperatures, making them well-suited for high-power applications. Metallic substrates can provide added mechanical stability in high-stress applications, and the reduced weight of MCPCBs makes them ideal for aerospace and portable electronic devices.
The choice of metal-core material is a critical consideration based on several factors, including thermal conductivity, weight, and cost. While aluminum and copper are the most frequently used materials in MCPCBs, other materials such as silver and nickel may also be utilized based on their unique properties.
Ceramic substrates
Ceramic PCB substrates, also known as ceramic printed circuit boards, are electronic substrates made of ceramic materials that are used in high-performance and high-reliability applications. These substrates consist of a thin layer of conductive material (usually copper) that is deposited on a ceramic base material. The ceramic material serves as the insulator between the conductive layers, allowing for the creation of a circuit.
Advantages of Using Ceramic Substrates in PCB Manufacturing
● High thermal conductivity: Ceramic substrates have excellent thermal conductivity, which allows for efficient dissipation of heat, making them ideal for high-power applications.
● Low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE): Ceramic substrates have a low CTE, which means they do not expand or contract significantly with temperature changes. This property makes them more stable and reliable in harsh environments.
● High mechanical strength: Ceramic substrates are highly durable and resistant to mechanical stress, ensuring that they can withstand repeated thermal cycles and vibrations.
● Good electrical insulation: Ceramic substrates have a high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, making them suitable for high-voltage and high-frequency applications.
● Chemical resistance: Ceramic substrates are highly resistant to chemical corrosives, making them ideal for use in harsh chemical environments.
● Compatibility with hermetic sealing processes: Due to their high melting points, ceramic substrates can withstand high-temperature hermetic sealing processes, ensuring excellent moisture and gas barrier properties.
Ceramic PCB substrates offer many benefits, including high thermal conductivity, low coefficient of thermal expansion, mechanical strength, good electrical insulation, and compatibility with hermetic sealing processes. They are commonly used in applications such as power electronics, LED lighting, automotive electronics, and aerospace.
Polyimide Substrates
Polyimide is a substrate commonly used in the manufacturing of flexible printed circuit boards (Flex-PCBs), offering several advantages over other materials.
Advantages of Using Polyimide Substrates in PCB Manufacturing
● Polyimide PCBs possess exceptional heat resistance, rendering them highly suitable for high-temperature applications. The material’s resistance to solvents and acids, in addition to its durability, make it a suitable choice for harsh environments subjected to chemical exposure.
● Flexibility is another major advantage of polyimide, making it ideal for use in applications that require bending, folding, or twisting. Polyimide is also lightweight, reducing the overall weight of the Flex-PCB assembly.
● Finally, polyimide’s electrical insulation properties improve the electrical performance of Flex-PCBs, making it a widely favored material for such applications.
Altogether, the outstanding combination of high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, flexibility, lightweight, and superior electrical performance has made polyimide a top choice for Flex-PCBs in numerous industries.
PCB Substrate Properties
PCB substrate properties are important factors to consider when choosing the right substrate material. Here are some important properties of PCB substrates:
● Dielectric constant: This property determines the ability of the substrate to store electrical energy. A low dielectric constant substrate is preferred for high-frequency applications, while a higher dielectric constant substrate is suitable for low-frequency applications.
● Thermal conductivity: This property refers to the substrate’s ability to transfer heat. A substrate with high thermal conductivity is preferred for applications that generate a lot of heat, as it helps to dissipate the heat.
● Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE): This property refers to the change in size of the substrate due to thermal expansion or contraction. A substrate material with a similar CTE to the components being mounted on the PCB can help prevent stress and cracking in the joints.
Other important properties include dimensional stability, moisture absorption, and chemical resistance, all of which can affect the performance and reliability of the finished PCB.
As a PCB design engineers, we should prioritize their knowledge of substrate properties to select a high-quality material for their circuit boards. Factors such as the substrate’s dielectric constant, thermal conductivity, and coefficient of thermal expansion can significantly impact the performance of the PCB. It’s also important to carefully consider the thickness of the substrate, as it can affect the board’s durability, impedance, and other critical characteristics.
In addition to the properties of the substrate, you should also consider some important characteristics of the substrate. Here are some important characteristics below:
| PCB Material | Typical Usage | DK | Tg (oC) | Recommended Board Type |
| FR-4 | Substrate, Laminate | 4.2 to 4.8 | 135 | Standard |
| CEM-1 | Substrate, Laminate | 4.5 to 5.4 | 150 – 210 | High Density |
| RF-35 | Substrate | 3.5 | 130 | High Density |
| Teflon | Laminate | 2.5 to 2.8 | 160 | Microwave, High Power, High Frequency |
| Polyimide | Substrate | 3.8 | >= 250 | High Power, Microwave, High Frequency |
| PTFE | Substrate | 2.1 | 240 to 280 | Microwave, High Power, High Frequency |
How to Choosing a Right PCB Substrates ?
Choosing the right PCB substrate depends on several factors, including the requirements of the specific electronic circuit and the intended application. Here are some considerations to keep in mind when choosing a PCB substrate:
● Frequency of operation: A substrate with a low dielectric constant is preferred for high-frequency applications.
● Power handling capacity: Substrate with high thermal conductivity, such as metal-core substrates, is needed for high-power applications.
● Thermal management requirements: A substrate with a high thermal conductivity is preferred for applications that generate a lot of heat.
● Cost and availability: The substrate material should be cost-effective and readily available.
● Design constraints: The substrate size, thickness, and shape can affect the design and layout of the PCB.
● Environmental conditions: The chosen substrate material should be able to withstand the environmental conditions where the PCB will be used, such as temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure.
Matching the properties of the PCB substrate with the specific requirements of the application and the electronic components being used is essential to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of the finished PCB.
Advancements in PCB Substrate Technology
There have been several advancements in PCB substrate technology that have led to improvements in the performance and reliability of electronic circuits. Some of these advancements include:
● Increasing use of high-performance substrate materials such as Rogers substrates, which offer better electrical and thermal properties than traditional FR-4 substrates.
● Development of low-loss substrate materials for high-frequency applications, which improve signal integrity and minimize signal distortion.
● Advances in thermal management, such as the use of metal-core substrates and exotic thermal interface materials, which enable more efficient heat dissipation from the electronic circuit components.
● Advancements in miniaturization, where thinner and smaller substrate materials are being developed to meet the demands of modern electronics.
● Improvements in environmental sustainability, where new PCB substrate materials with biodegradable or recyclable properties are being developed to reduce waste.
Therefore, advancements in PCB substrate technology are helping to increase electronic circuit performance while reducing cost and environmental impact.
Where to Manufacture PCBs ?
For those in need of high-quality printed circuit board manufacturing and assembly services, JarnisTech is an excellent choice. With over a decade of experience and a client base exceeding 2,500 worldwide, JarnisTech has established itself as a trusted leader in the industry.
Our company employs a team of highly skilled engineers and utilizes specialized equipment to ensure that client requests are met with precision and efficiency. Clients can benefit from several advantages when partnering with JarnisTech, including the ability to choose between rigid or flexible PCBs depending on their specific requirements.
Furthermore, clients have the freedom to customize their orders by specifying details such as the number of layers, copper and board thickness, and other relevant parameters. The ordering process is designed to be straightforward, allowing clients to submit their demands and receive a quote within eight working hours. The company offers secure worldwide shipping through reputable courier services such as FedEx, DHL, EMS, and TNT.
Summary
PCB substrates play a critical role in the performance and reliability of electronic circuits. Selecting the right substrate material is essential to ensure optimal performance, thermal management and cost-effectiveness. Advancements in PCB substrate technology have led to the development of new substrate materials with improved electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, as well as miniaturization and environmental sustainability. As electronic circuits become more complex and demanding, the importance of choosing the right PCB substrate material will continue to increase.
JarnisTech Technology is a premier destination for top-notch Printed Circuit Board (PCB) manufacturing and assembling services. Our highly skilled team of experts employs a meticulous approach to customer demands, ensuring that all requirements ranging from application environments to product performance are met. Prior to commencing the manufacturing process, our engineers carefully consider all facets of the project to provide optimal PCB solutions to our esteemed clients.
We place great emphasis on quality control to assure customer satisfaction. Every circuit board undergoes rigorous testing before being cleared for shipping. Our team strives to achieve customer contentment by delivering the highest quality PCB products and services possible.
We encourage clients to act upon their product ideas with great urgency by obtaining an instant quote to commence their projects with JarnisTech Technology. Allow us to help you bring your product vision to life.
Related Posts:
1. Selecting PCB Laminate Materials: A Comprehensive Overview
2. PCB Copper Trace Width and Space: Everything You Need to Know About Them
4. What Is Fiberglass PCB and Why Fiberglass Used in PCB Manufacturing?
5. Standard PCB Thickness-Choosing the Correct Thickness for PCB
