JarnisTech, a renowned Chinese manufacturer, has established a strong presence in the heater PCB industry for numerous years. Our unwavering commitment to delivering exceptional quality has been affirmed by countless satisfied clients worldwide. With an unyielding focus on customer satisfaction, we consistently strive to provide unparalleled services to our esteemed clientele.
At JarnisTech, we take pride in offering heater PCBs that exemplify superior craftsmanship. Our products are meticulously tested and proven and have a proven track record for delivering stellar performance and steadfast reliability. Thanks to our adoption of cutting-edge manufacturing techniques, we’ve managed to attain exemplary soldering properties at decreased temperatures. This not only enhances the overall quality of our heater PCB but also minimizes the risk of PCB thermal stress, resulting in prolonged product lifespan.
Furthermore, our dedication to continuous improvement enables us to streamline production processes, significantly reducing manufacturing time.This translates into in expedited delivery times for our PCB manufacturing, facilitating a rapid and proficient progression of our clients PCB projects.
As industry leaders, we remain committed to upholding the highest standards of professionalism, product excellence, and customer satisfaction. With JarnisTech, you can trust that our heater PCBs will meet your exacting requirements, providing optimal heating performance and peace of mind.
What is Heater Circuit boards?
A heater PCB board, known as a control board or furnace control board plays a role in a heating system by control and regulating the heating process.
The heater circuit board is essentially the brain of the heating system. the heater circuit board captures signals from the thermostat, handle the collected data, and transmits signals to diverse elements within the heating system. These signals facilitate the initiation and halt of heating, the regulation of temperature, among other functions.
Typically, a heater circuit board includes:
Microprocessors: These are the ‘brains’ of the control board. They process the signals from the thermostat and send the appropriate commands to the rest of the heating system.
Relays and switches: elements within the setup, receive directives from the microprocessor which prompt them to initiate or halt operations of the heater, fan, and other associated components as necessitated.
Circuitry: This includes various electric paths and connections that allow signals to move throughout the board.
Connectors: It embody the junctures at which the control board interacts with different elements of the heater system. These elements include the thermostat, the blower motor and the ignitor.
Problems involving a heating system can be pinned back to complications with the heater PCB circuit board. Such as malfunctioning relay, a blown-out microprocessor, or a disrupted circuit. If the heater circuit board is not operating optimally, it could potentially lead to the entire heating system becoming non-functional.
Remember that working with a heater circuit board should ideally be done by a trained professional, as it involves working with potentially dangerous electrical currents and complex equipment.
What Materials are Used to Manufacture Heater PCB?
Heater Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) typically utilize a foundational material, like fiberglass-reinforced epoxy (FR4), imparting structural stability. Upon the surface of this PCB, heating elements are fashioned using conductive substances like copper and form resistive traces or pads. These heating constituents are linked to the power source via circuitry and their operation can be regulated using temperature sensors, thermostats, or programmable controllers.
Main Functions of Heater PCB:
Heater PCBs are primarily used to generate heat in a controlled manner. They incorporate heating components, for instance, resistive traces or pads, which transmute electrical energy into heat. This produced heat can be harnessed for diverse uses, encompassing temperature moderation, thermal management, fluid or gas heating, and upholding certain operational conditions.
Types of Heater PCBs
There are many types of heater Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) exist, each one specially crafted to meet particular applications and heating prerequisites. A few common types include:
Etched Foil Heater PCBs:
Etched foil heaters consist of a resistive foil element patterned on a PCB substrate. This foil is usually composed of materials like copper or nickel-chromium alloy. These heaters provide stellar heat transfer, adaptability in terms of shape and size, and uniform heat dispensation. They are prevalently employed in various scenarios like medical devices, laboratory apparatus, and industrial heating applications.
Silicone Rubber Heater PCBs:
Silicone rubber heaters incorporate a sleek, flexible heater component encapsulated within a silicone rubber sheet, typically composed of resistance wire or etched foil. These heaters exhibit lots of flexibility, high resistance to moisture, and superb thermal insulation properties. They’re utilized in fields such as automotive, aerospace, food processing, and electronics.
Kapton Heater PCBs:
Kapton heaters utilize a thin, flexible polyimide film as the substrate, with a resistive element embedded or printed onto its surface.These heaters are noted for their excellent temperature resistance, light weight and robust dielectric strength.
Carbon Film Heater PCBs:
Carbon film heaters utilize a carbon-centric resistive film laid on a PCB substrate. These heaters are recognized for their even heat distribution, robust thermal stability, and economical advantage. They are typically implemented in situations that involve heating pads, warming trays, and HVAC systems.
Thick Film Heater PCBs:
Thick film heaters use a thick layer of resistive ink printed onto a PCB substrate. These heaters provide excellent heat transfer, durability, and stability. They find applications in industrial heating, automotive systems, and consumer electronics.
Micro-etched Heater PCBs:
Micro-etched heaters leverage an exacting etching procedure to forge complex heating patterns on a PCB, widely recognized for their high power density, swift heat transfer, and accurate temperature regulation. They find typical usage in sectors such as semiconductor processing, medical devices, and aerospace
It’s important to note that the specific type of heater PCB chosen depends on factors such as the desired heat output, temperature range, flexibility requirements, and the target application’s environmental conditions. Manufacturers often provide customizable options to meet specific customer needs.
Design Considerations for Heater PCBs
During the development of heater PCBs, numerous factors require meticulous consideration to guarantee peak functionality and dependability. Here are some crucial design contemplations to bear in mind:
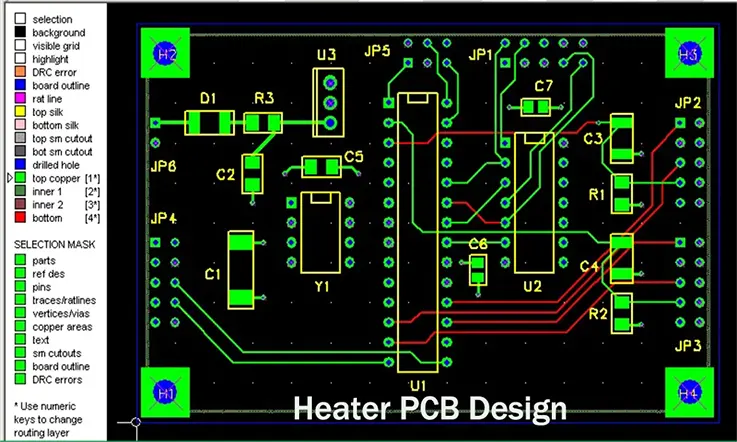
Thermal Management:
The significance of Efficient heat dispersion is paramount for heater PCBs. Appropriate thermal control methodologies, including the correct allocation of heat sinks, thermal vias, and thermal pads, ought to be integrated within the design to subdue overheating and maintain optimal thermal efficiency.
Material Selection:
The selection of appropriate materials for the PCB is paramount. Top-tier, thermally tolerant substrates and copper layers with superior thermal conductivity are favored to promote efficient heat transfer. Additionally, opt for materials boasting excellent electrical insulation properties, a key element for ensuring safety and dependability
Circuit Layout and Traces:
The layout of the heater circuit should be designed to minimize resistance and maximize heat distribution. Optimal arrangement of traces and components can facilitate evenly distributed heating across the PCB. Account for the current carrying capacity of traces and guarantee their ability to sustain the necessary power without considerable voltage dips or overheating
Power Requirements and Voltage Considerations:
Understanding the power requirements of the heater is vital for designing the PCB. The circuit should be designed to handle the required power levels and voltage ratings. Inclusion of sufficient power supply and voltage control measures, like voltage regulators or current-restricting components, should be built into the design to warrant steady and secure operation.
Signal Integrity and Noise Considerations:
If the heater PCB includes other components or circuits, it is crucial to consider signal integrity and noise mitigation. Proper grounding techniques, signal shielding, and noise filtering should be employed to minimize interference and maintain reliable operation of the entire system.
Safety Measures:
Prioritizing safety is of utmost importance in the design of heater PCBs. The integration of features like over-temperature protection, short-circuit protection, and isolation barriers can contribute to hazard prevention and uphold user safety.
Environmental Factors:
Consider the operating environment of the heater PCB. Aspects like extreme temperatures, humidity, and contaminant exposure should be factored into the design process. The selection of suitable conformal coatings or encapsulation materials can offer extra protection against such environmental influences.
Through meticulous contemplation of these design factors, you can create heater PCBs that offer maximum efficiency, dependability, and safety for your specific applications. Collaborating with seasoned PCB designers and manufacturers can lend invaluable knowledge and skills to ensure a successful design.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for heater PCB involves several stages, including PCB fabrication, component placement and soldering, and testing and quality control. Here is an overview of the typical manufacturing process:
PCB Fabrication:

● Design Conception: Formulate an intricate design layout of the heater PCB, incorporating the positioning of components, circuitry traces, and essential elements.
● Preparation of PCB Substrate: Identify a suitable substrate material and ready it via cleaning and applying necessary coatings for enhanced conductivity or safeguarding.
● Imaging: Impose the PCB blueprint onto the substrate employing a photographic process to get the desired circuit design.
● Etching: Expel excess copper from the substrate using chemical etching that results in the desirable copper traces required for the heating circuit.
● Drilling: Fabricate holes in the PCB for accommodating components and establishing electrical linkages.
● Plating: Apply a sliver of conductive material, for instance, copper, to the fabricated holes and copper traces to augment conductivity.
● Surface Finish: Administer a protective surface finish to hinder oxidation and endorse component soldering.
Component Placement and Soldering:
● Component Selection: Choose the appropriate components for the heater PCB, considering specifications, compatibility, and reliability.
● Automated or Manual Placement: Components are either placed manually or using automated pick-and-place machines, depending on the production volume and complexity.
● Solder Paste Application: Apply solder paste to the PCB pads where the components will be soldered.
● Component Placement: Position the components accurately onto the solder paste using automated equipment or skilled technicians.
● Reflow Soldering: Subject the PCB to controlled heat to melt the solder paste, forming reliable electrical connections between the components and the PCB.
Testing and Quality Control:
● Visual Inspection: Scrutinize the soldered PCB to detect any discernible imperfections, such as components out of alignment or solder bridges.
● Functional Testing: Authenticate the performance of the heater PCB by implementing suitable electrical signals and determining the desired heat output.
● Electrical Testing: Undertake exhaustive electrical assessments to guarantee accurate connections, signal integrity, and compliance with the defined electrical parameters.
● Quality Control: Execute meticulous quality assurance procedures across the manufacturing process, inclusive of inspections, metric evaluations, and in line with industry benchmark standards.
Final Assembly and Packaging:
●Final Inspection: Conduct a final inspection to confirm the successful completion of all fabrication and assembly operations, and to verify that the PCB Board adheres to the stipulated technical requirements.
● Cleaning: Remove any residues or contaminants from the PCB surface using appropriate cleaning methods.
● Packaging: Package the heater PCBs securely, considering protection from environmental factors and transportation requirements.
By following these manufacturing steps and maintaining strict quality control measures, PCB manufacturers can ensure the production of reliable and high-quality heater PCBs that meet the specific requirements of their customers.
Advantages and Applications of Heater PCB
Advantages of Heater PCBs:
Compact Size
Efficient Heat Transfer
Fast Response Time
Customizability
Energy Efficiency
Applications of Heater PCBs:
Industrial Heating
Medical and Laboratory Equipment
Automotive Systems
Consumer Electronics
Aerospace and Defense
Greenhouse and Agriculture
Energy and Sustainability
These are just a few examples of the wide range of applications where heater PCB Board offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, flexibility and precise heating capabilities. The multifaceted nature of heater PCB renders them a fitting choice for an array of sectors and a breadth of heating equipment
Why Choose Us?
JarnisTech: The Best Heater PCB Manufacturer And Supplier In China
When it comes to selecting the finest heater PCB for your business or projects, JarnisTech stands out as the optimal choice. With our extensive range of heater PCB offerings, we have established ourselves as a prominent manufacturer and assembler in the industry.
At JarnisTech, our relentless pursuit of superior quality and bespoke solutions has merited us the confidence of clients globally. Being a front-runner in the heater PCB industry located in China, we take honor in supplying products that satisfy stringent quality control parameters. Our commitment to distinction guarantees that every PCB and PCBA boards we manufacture complies with the most rigorous industry standards.
We grasp the criticality of cost-efficiency in the highly competitive market landscape we navigate today. Therefore, we have carefully priced our products to offer affordability without compromising on quality. Choosing JarnisTech promises an impressive value proposition for your investment.
Furthermore, we recognize that every project may have unique specifications. To cater to these individual needs, JarnisTech offers customization services. Our skilled professionals are equipped with the expertise to tailor our heater PCB solutions to meet your specific requirements. This flexibility sets us apart as a reliable partner in fulfilling your project’s demands.
Choose JarnisTech as your trusted PCB manufacturer, and experience the benefits of our unbeatable quality, cost-effectiveness, and customer-centric approach. Contact us today to explore our comprehensive range of heater PCB solutions and discuss how we can best serve your business or project needs.
Related Posts:
2.What is a Round Printed Circuit Board (PCB)?
3.Waterproof PCBs: Everything You Should Know
