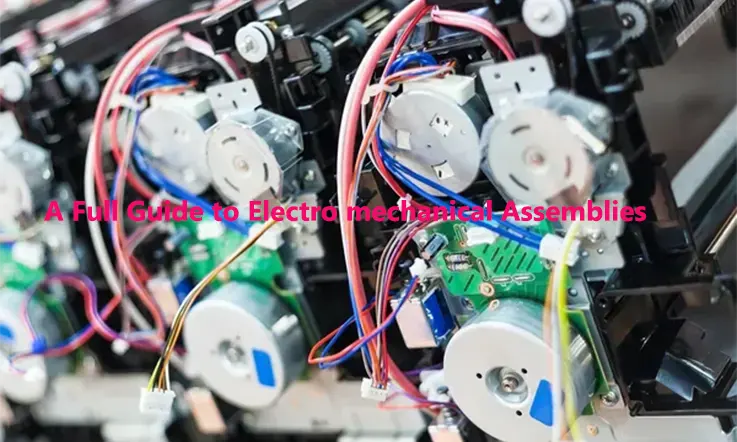
JarnisTech is a distinguished provider of electromechanical assemblies, which are essential components in electrical and electronic systems utilized across various industries, including aerospace, communications, military, and power generation. These assemblies combine electrical circuitry with mechanical parts, and their design and construction must be approached with great care to ensure optimum functionality and manufacturability. Electromechanical assemblies can range from simple to highly complex, and a thorough understanding of their types and applications is vital. In this guide, our team of experts has compiled comprehensive information on electromechanical assemblies, including their definition, available types, and the industries and applications where they are utilized.
What Is An Electro Mechanical Assembly ?
Electro-mechanical assemblies are an amalgamation of electronic and mechanical components housed together in a consolidated package. These assemblies encompass subsystem assemblies that incorporate board-level interconnects and chassis wiring, as well as full system assemblies known as box builds. The range of electro mechanical assemblies is diverse, including box builds, chassis, enclosures, DIN rail assembly, LED assembly, fan trays, switch assembly, fan modification, power panel assemblies, and fan assembly.
There are also specific mechanical assembly products, such as displays, barcode readers, blowers, fans, and terminal blocks, which can be integrated into electro mechanical assemblies for enhanced functionality.
Electro mechanical assemblies are extensively utilized in various industries and applications, including medical, clean technology, industrial, computers, homeland security, communications, marine, test and instrumentation, and satellite communications. The diversity of these applications illustrates the significance of electro mechanical assemblies in modern technology and highlights the need for their reliable design and manufacturing to ensure optimal performance.
Types of Electromechanical Assemblies
Electromechanical assemblies are specifically designed and constructed to perform a particular function. Some of the most commonly manufactured electromechanical assemblies include:
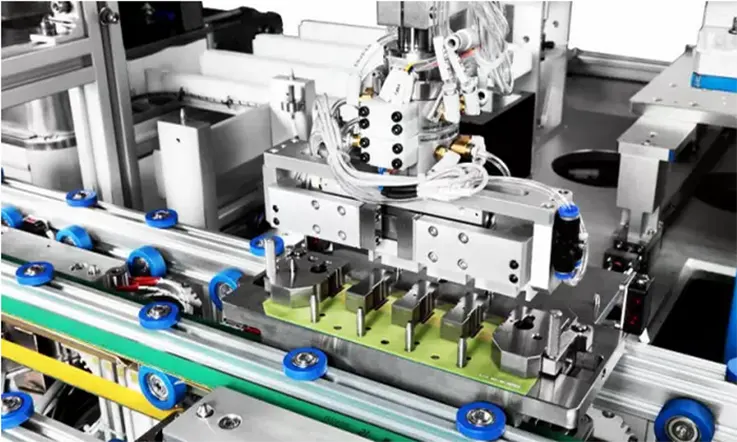

Cable and Harness Assemblies: Cables and harness assemblies comprise cables or wires that transmit electrical power or signals.
Transformer Assemblies: Transformers transfer electrical energy between two or more electrical circuits. They increase or decrease the voltage level according to the requirements of the application.
Power Supply Assemblies: Power supplies provide electrical power to at least one electric load by converting a current to the correct format and voltage required to power it. Power supplies can be designed as standalone devices or incorporated into appliances.
DIN Rail Assemblies: DIN rails, also known as mounting rails, are used to mount other components within an electromechanical assembly. They must be configured according to the components and subassemblies.
Panel Assemblies: Some electromechanical assemblies are integrated into panels, which serve as a means of controlling the distribution of electrical power into connected circuits.
Switch and Sensor Assemblies: Two vital components of electronic systems are switch assemblies and sensor assemblies. Switch assemblies typically connect or disconnect a power supply to electrical components, while sensor assemblies convert stimuli, such as sound, heat, light, or motion, into electrical signals.
Components used in Electro Mechanical Assemblies
Electromechanical assemblies are devices that combine electrical and mechanical components to perform a specific function. There are many different types of electromechanical assemblies, including:
Relays: These are simple electromechanical devices that use an electromagnetic coil to switch a set of contacts on or off. Relays are commonly used in applications such as control systems, safety devices, and power distribution.
Solenoids: Solenoids are electromechanical devices that use a magnetic field to move a plunger or valve. They are often used in automotive, industrial, and medical applications.
Actuators: Actuators are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. They can be used to move valves, switches, or other mechanical components.
Motors: Motors are devices that convert electrical energy into rotational motion. They are used in a wide range of applications, including manufacturing equipment, robotics, and transportation.
Sensors: Sensors are devices that detect changes in their environment and convert them into electrical signals. They can be used to measure temperature, pressure, position, and many other variables.
Generators: Generators are devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. They are used in power generation, renewable energy systems, and backup power systems.
Transformers: Transformers are devices that transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another using magnetic induction. They are used to step up or step down voltage levels in power distribution systems.
Actuated valves: Actuated valves are valves that are operated by an actuator, which can be electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic. They are used in a wide range of industrial applications, including chemical processing, oil and gas, and water treatment.
These are just a few examples of the many types of electromechanical assemblies that are used in various industries.
Assembly Process of Electro Mechanical Assemblies
The assembly process of Electro Mechanical Assemblies involves several steps, including planning and preparation, component placement and fastening, wiring and soldering, and testing and quality control. Here is a more detailed breakdown of each step:
1. Planning and Preparation: This step involves reviewing the design specifications and determining the required components and tools. The assembly technician will also plan the assembly sequence and make sure all necessary materials and tools are available.
2. Component Placement and Fastening: In this step, the assembly technician places the components in their designated locations and fastens them using screws, bolts, or other fasteners. It is important to ensure that all components are properly aligned and secured to prevent any potential issues during operation.
3. Wiring and Soldering: Once the components are in place, the wiring and soldering process begins. The assembly technician will connect the electrical and electronic components as per the design specifications, and solder them in place using a soldering iron. It is crucial to ensure that all connections are properly made and that there are no loose wires or cold solder joints.
4. Testing and Quality Control: Once the assembly is complete, it undergoes testing and quality control to ensure that it meets the required specifications. The assembly technician may use various testing equipment such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, and function generators to verify the assembly’s performance. Any issues are identified and corrected, and the assembly is retested until it meets the required specifications.
Overall, the assembly process of Electro Mechanical Assemblies requires precision, attention to detail, and careful testing to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications and performs as expected.
Electro Mechanical Assembly By Outsourcing
Electromechanical assembly work is a complex process that involves assembling various electrical and mechanical devices that interact with each other and respond to received signals. These devices include control panels, controllers, sensors, compressors, and more. Assembling such complex systems requires expertise in design, assembly, and operation of electro mechanical products.
If your company lacks the necessary expertise, outsourcing the electro mechanical assembly work to a specialized contractor like JarnisTech is an excellent choice. By doing so, you can fill the expertise gap in your company and focus on other aspects of your business.
At JarnisTech, we possess extensive knowledge of various electrical and mechanical devices, and we have provided electro mechanical assembly services to customers across a wide range of industries. Our team of engineers collaborates with you throughout the project to deliver a custom-tailored solution, no matter how complex the assembly work may be. We ensure that you receive a high-quality electro mechanical assembly service that meets your requirements precisely.
Our Capabilities in Electro Mechanical Assembly
JarnisTech is a leading provider of electromechanical assemblies, with expertise in handling a wide range of assemblies, including PCB assemblies (BGA, uBGA, CSP), cable assemblies, and box build assemblies. Our team specializes in various electromechanical assembly techniques, such as Surface Mount Technology, Through-hole Technology, Additive Manufacturing, Complex RF Electro-Mechanical, and more.
Our state-of-the-art in-house CNC machining capabilities enable us to manufacture parts with different geometric shapes using advanced 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines. This gives us the flexibility to provide customized solutions to meet the specific needs of our clients.
At JarnisTech, we never compromise on quality and perform stringent inspection and testing processes to ensure that our products meet the highest standards. Our testing and inspection processes include Solder Paste Inspection, Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray Inspection, Visual Inspection, In-circuit Testing, Functional Testing, and more.
Our commitment to quality and expertise in electromechanical assembly techniques make us a reliable partner for any project. We work closely with our clients to provide tailored solutions that meet their unique requirements, resulting in high-quality products that exceed their expectations.
Why Choose Us ?
Our commitment to quality assurance is reflected in our adherence to the highest quality standards. Our certificates, including ISO9001, ISO 13485, IPC, and UL, serve as a testament to the exceptional quality of our assemblies.
We pride ourselves on our high level of flexibility, which enables us to deliver customized assembly services tailored to meet the unique needs of each customer. Our flexibility allows us to handle various electromechanical assembly needs, from simple to complex.
Our strong network of suppliers enables us to source high-quality components quickly and efficiently, based on the specifications provided by our customers. This helps simplify supply chains and reduces costs for our customers.
At JarnisTech, we understand the importance of on-time delivery and are committed to meeting our customers’ deadlines. Our state-of-the-art facilities and streamlined in-house manufacturing processes allow us to deliver electro mechanical assemblies to our customers on time, every time.
Importance of Testing and Inspection in Electro-Mechanical Assemblies
Testing and inspection are crucial steps in the electro-mechanical assembly process. They ensure that the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards, and they help to identify and eliminate defects and failures that can lead to costly rework, recalls, or even safety hazards. Here are some specific reasons why testing and inspection are important in electro-mechanical assemblies:
Verification of Functionality: Testing ensures that the electro-mechanical assembly performs its intended function correctly. It verifies that all components are connected and functioning as expected, and it detects any malfunctions or errors that may occur during operation.
Detection of Defects and Failures: Inspection helps to detect defects and failures that may occur in the electro-mechanical assembly. These defects may be due to manufacturing defects, design flaws, or environmental factors. By identifying these defects early on, they can be corrected before the assembly is shipped or installed.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations: Testing and inspection help to ensure that the electro-mechanical assembly meets the relevant industry standards and regulations. These standards may include requirements for safety, performance, reliability, and environmental impact.
Quality Assurance: Testing and inspection are essential for maintaining the quality of the electro-mechanical assembly. They help to identify and correct any deviations from the expected quality level, and they provide a way to monitor and improve the quality of the assembly over time.
Cost Savings: Testing and inspection can save money by reducing the need for rework, recalls, and warranty claims. By identifying and correcting defects early on, they can prevent costly delays and repairs, and they can improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the assembly process.
Therefore, testing and inspection are critical steps in ensuring that electro-mechanical assemblies meet the required standards and specifications, and they help to prevent defects and failures that can lead to costly rework, recalls, or safety hazards.
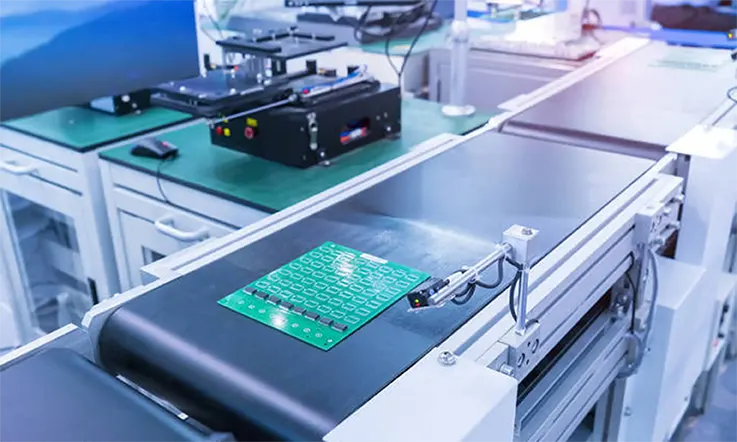
Industrial Applications of Electromechanical Assemblies
Electromechanical assemblies are used in a wide range of industrial applications due to their ability to combine electrical and mechanical components to perform specific functions. Some of the most common industrial applications of electromechanical assemblies include:

Manufacturing
Electromechanical assemblies are used in manufacturing equipment such as conveyors, robots, and assembly lines. They can be used to move parts, control processes, and ensure quality control.
Automotive
Electromechanical assemblies are used in automotive applications such as actuators for power windows and locks, sensors for airbags and anti-lock brakes, and motors for windshield wipers and power seats.
Aerospace
Electromechanical assemblies are used in aerospace applications such as actuators for landing gear and flight control surfaces, sensors for navigation and control, and motors for pumps and generators.
Energy and Power
Electromechanical assemblies are used in energy and power applications such as generators, transformers, and motors for power generation, distribution, and conversion.
Medical
Electromechanical assemblies are used in medical applications such as actuators for surgical instruments, sensors for patient monitoring, and motors for medical equipment such as pumps and ventilators.
Robotics
Electromechanical assemblies are used in robotics applications such as actuators for robot arms and grippers, sensors for navigation and control, and motors for movement and power.
Packaging
Electromechanical assemblies are used in packaging applications such as conveyors, sensors for product detection and tracking, and actuators for packaging equipment such as filling machines and labelers.
Agriculture
Electromechanical assemblies are used in agriculture applications such as actuators for irrigation systems, sensors for monitoring soil moisture and temperature, and motors for equipment such as tractors and harvesters.
These are just a few examples of the many industrial applications of electromechanical assemblies. They are widely used in many different industries due to their versatility and ability to meet specific application requirements.
Future of Electro Mechanical Assembly
The future of Electro Mechanical Assembly looks promising with the advancements in technology and the increasing demand for automation and robotics. Here are some potential developments that could shape the future of Electro Mechanical Assembly:
Miniaturization: With the increasing demand for smaller, lighter, and more efficient devices, Electro Mechanical Assemblies will continue to be miniaturized. This will require the development of new, smaller components and assembly techniques.
Automation: Automation in Electro Mechanical Assembly will increase, with the use of robotics and other automated systems to perform tasks such as component placement, soldering, and testing. This will lead to faster, more efficient assembly processes and higher productivity.
Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is already being used in some Electro Mechanical Assemblies, and this trend is expected to continue. 3D printing will enable the production of complex geometries and customized parts, reducing the need for assembly of multiple components.
Integration with Electronics: There will be an increased integration of Electro Mechanical Assemblies with electronics, as the lines between mechanical and electronic components continue to blur. This will require new skills and knowledge for assembly technicians.
Sustainable Manufacturing: There will be a growing focus on sustainable manufacturing in Electro Mechanical Assembly, with a shift towards the use of environmentally friendly materials and processes. This will require the development of new, sustainable assembly techniques and materials.

Conclusion
Electro Mechanical Assembly is a critical process in the manufacturing of a wide range of products, from simple switches to complex control systems. It involves the assembly of mechanical, electrical, and electronic components to create functional systems that meet specific requirements.
The types of Electro Mechanical Assemblies can vary from basic to complex, depending on the application and required functionality. As technology advances, the future of Electro Mechanical Assembly looks promising, with developments such as miniaturization, automation, additive manufacturing, integration with electronics, and sustainable manufacturing expected to shape the industry.
Overall, Electro Mechanical Assembly plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing, and its continued evolution and innovation will enable the creation of new and exciting products that meet the needs of an ever-changing world.
Related Posts:
- Mixed PCB Assembly Technology Services For Your Next New Project
- Why Electronic Potting is So Important in PCB Assembly?
- What Is Printed Circuit Boards Assembly?
- Cable and Wire Harness Assembly
- Electronics Components PCB Assembly
- China:The Best PCB Consignment Assembly Services At JarnisTech
- PCB Box Build Assembly
- Nine Method of Save Cost PCB Assembly Production
- How Many Types of Turnkey PCB Assembly?
