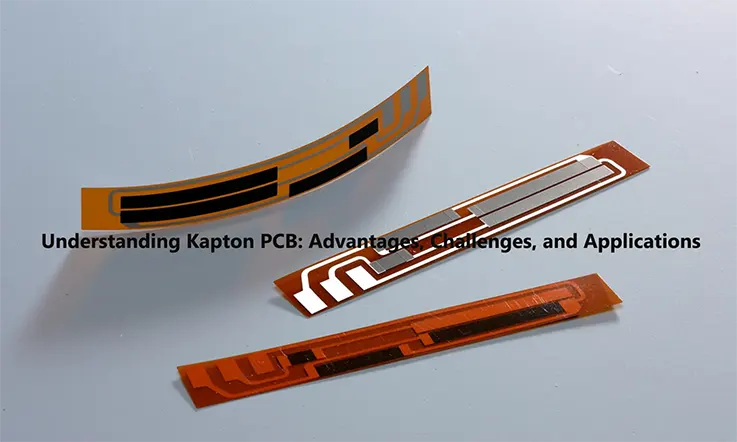

Kapton PCB is a progressive technology, revolutionizing our perspectives and methodologies towards the design of printed circuit boards. Amid the escalating demand for advanced electronics that exhibit varied form factors and enhanced performance, Kapton PCB has surfaced as a multifaceted solution, adept at catering to the distinct needs of an extensive array of applications.
Steering clear of the traditional FR-4 material, Kapton PCB implements flexible Kapton film as the base, conferring excellent resistance to extreme temperatures, dampness, chemical influences, radiation, and other prevailing environmental conditions. This elevates Kapton PCB as a preferred option across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and industrial machinery, where the need for reliability and durability is imperative.
In this discourse, we’ll unearth both the benefits and difficulties associated with the deployment of Kapton PCB. Furthermore, we’ll confer salient inputs to contemplate when determining the employment of Kapton PCB for specific requirements. Concurrently, we will broach the subject of the paramount importance of Kapton PCB within the electronics landscape, and their pivotal role in revolutionizing the domain of blueprinting and production.
What is Kapton?
Kapton is a type of polyimide film, which is a polymer used in the creation of flexible printed circuit boards. Its origination in the 1960s is associated with the distinguished DuPont Corporation, a prime producer of industrial chemicals and materials. The impetus navigating the advancement of Kapton was the imperative need for a PCB having the resilience to endure high temperatures.
Amid the manufacturing course, it was discerned that Kapton manifests extraordinary constancy across a substantial continuum of temperatures, going as low as -452 degrees Fahrenheit and peaking at 752 degrees Fahrenheit. Moreover, this material exhibits remarkable resilience against different types of mechanical strains. It is reasonable to argue that Kapton has played a pivotal role in enabling the creation of lightweight, portable appliances, foldable gadgets, and compact electrical systems that are prevalent in modern technology.
What is Kapton PCB?
Printed circuit boards are indispensable elements in electronic apparatuses, furnishing an infrastructure for the mechanical support and connection of electronic components, facilitated by the utilization of conductive pathways and traces laminated with copper. These boards are crucial for the proper transmission of signals within electronic devices.
Flexible printed circuit boards further enhance this technology by providing customized interfaces based on specific requirements. FPCB can be made using flexible polyamides, such as Kapton, as the base material to allow for flexibility. A conductive pattern of traces is applied to a thin layer of Kapton polymer film, enabling the creation of a highly flexible printed circuit board.
The genesis of FPCB technology traces back to the timeline succeeding World War II, and its evolution remains in constant motion within the industry. Electronic gadgets frequently encounter severe temperature conditions, potentially exceeding their threshold, leading to their eventual degradation unless the suitable materials are utilized. Since 1960, Polyimides, such as Kapton, have been the preferred solution since 1960 due to their ability to withstand high temperature conditions.
Kapton stands as an optimum substance for electrical apparatuses accredited to its exceptional thermal resistance. Being flame-resistant, it retains its structural integrity and performance under exposure to temperatures scaling up to 700 Fahrenheit. Moreover, its extensive adaptability earmarks it as an exceptional option for crafting efficient circuit board labeling, even under the harshest of conditions.
FPCB can vary in complexity, ranging from single-layered to double-layered, but the polyimide Kapton material consistently serves as the base layer in all FPCB. It provides superior flexibility and reliability, ensuring that the printed circuits function optimally in electronic devices under challenging conditions.
Types of Kapton PCB
Kapton PCB offer a plethora of versatile types that are extensively used in various industries such as the military, medical, and mobile phone industries. These types serve diverse purposes, making Kapton PCB a highly versatile material. Its most noteworthy types include:
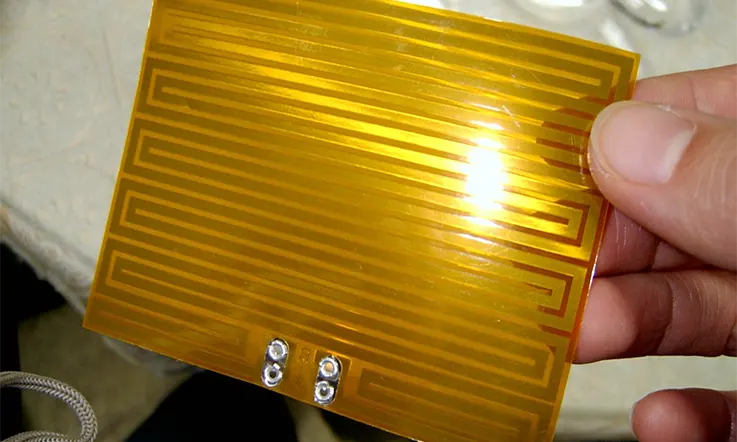
● Flexible PCB
● Kapton film PCB
● Blank single PCB
● Medical Controller Flex PCB
● Kapton heater with adhesive PCB
Advantages of Kapton PCB
● Flexible Design: Kapton PCB demonstrate a superior degree of flexibility and bendability, which is essential for some electronic devices and applications. Kapton PCB outperforms conventional PCB by delivering amplified flexibility, all the while sustaining robust durability.
● Durable and High Endurance: Kapton PCB exhibits commendable resistance towards physical strain and possess high durability, ensuring augmented longevity and reliability under various severe environmental circumstances.
● High Thermal Stability: Kapton PCB are designed to endure elevated temperatures while maintaining their functionality without any detriment. This capability makes them suitable for electronic devices that operate under extreme heat conditions.
● Efficient Signal Movement: Kapton PCB facilitates the efficient maneuvering of signals within electronic apparatus, thereby augmenting their comprehensive performance and reliability.
● Increased Power Efficiency: Kapton PCB bolsters the power efficiency of electronic devices, thereby diminishing power consumption and, consequentially, the corresponding power cost.
Applications of Kapton PCB
Kapton PCB are used in a variety of electronic devices that require flexibility, durability, and temperature resistance. Some common applications include:
●Aerospace
●Devices
●Automobile sector
●Electronics for consumers
●Industrial equipment
Overall, Kapton PCB are becoming increasingly popular in various industries due to their high temperature tolerance, durability, and flexibility.
Why Choose Kapton PCB Material in Manufacturing Process?
Kapton PCB demonstrate considerable advantages in diverse manufacturing applications, largely due to their distinctive thermal resistance characteristics. The following are additional justifications for selecting Kapton PCB as a prime choice:
● Optimal Electrical Performance: Kapton PCB are tailored to form flexible circuits delivering outstanding electrical performance, guaranteeing an unimpeded transmission of electrical impulses.
● High-Density Mounting: Kapton PCB can accommodate both high- and low-density mounting configurations, offering enhanced flexibility in application.
● Simple Assembly Process: The polyimide material used in Kapton PCB simplifies the electrical assembly process, leading to improved efficiency and time-saving in production.
Our proficient team stands poised to address any inquiries or challenges you might confront pertaining to PCB. We encourage you to connect with us without reservation at your earliest convenience.
How to Manufacture a Kapton PCB?
● Design and layout: The desired circuit pattern is designed using computer-aided design software, and the layout is optimized for the Kapton substrate.
● Cleaning and preparation: The Kapton base is meticulously cleaned and readied to ensure it is very clean from any potential contaminants, which could influence the copper layer’s adherence.
● Applying the copper layer: Utilizing a procedure known as sputtering or electroplating, a slim layer of copper is deposited onto the Kapton base. This will constitute the conducting paths of the circuit.
● Chemical Etching: The process of chemical etching is utilized to eliminate unwanted copper traces from the substrate, retaining only the requisite conductive paths.
● Drilling: Drilling are incorporated into the Kapton base substrate to facilitate mounting and connection of critical components through the circuit.
● Plating and finishing: The exposed copper traces and holes are plated with a thin layer of metal such as gold or tin to enhance their conductivity and deter oxidation. Subsequently, the PCB is enveloped with a protective coating to safeguard it from harm and fortify its resilience against environmental influences.
● Testing: The finalized Kapton PCB undergoes rigorous testing to guarantee that it aligns with predetermined specifications and operates effectively.
Types of Polyimide Used in Kapton PCB
Polyimide feature prominently in the production of Kapton PCB owing to their outstanding thermal, mechanical and electrical attributes. The construction of these PCB employs a variety of polyimides, each boasting distinct characteristics. Provided herein is a synopsis of the varied types of polyimide incorporated in the fabrication of Kapton PCB:
● Pure Polyimide: known as a second generation polyimide refers to polyimides that’re completely devoid of additives and brominated flame retardants. They exhibit thermal stability and boast higher resistance to heat when compared to many modern alternatives.
● Third-Generation Polyimides: These polyimide are characterized by the inclusion of additives to bolster their resistance to flammability, rendering them a prime choice for mitigating electrical fires. Nonetheless, they generally demonstrate reduced thermal stability compared to pure polyimide, and their manufacturing time is less extensive.
● Filled Polyimide: These polyimide, as indicated by their designation, incorporate an additional filler element alongside the polyimide itself. The filler is used to minimize resin shrinkage, averting the formation of cracks during the curing and drilling stages.
● Low-Flow Polyimides: These polyimides feature various fillers that restrict their flexibility, such as flow restrictors and resins. They are used where reduced flexibility is required.
Which One is Better : Kapton PCB and FR-4 PCB?
Materials made of Polyimide, frequently referred to as Kapton PCB, provide eminent advantages when contrasted with FR-4 materials in a range of electronic applications.
● Exceptional Tensile Strength: With an impressive tensile strength approximating 231 MPa, Kapton PCB significantly surpasses FR-4 PCB, which stands around 70 MPa. Consequently, Kapton PCB demonstrates a superior strength relative to FR-4, qualifying them as apt for diverse electronic applications.
● Flexibility: The core material of Kapton PCB, Polyimide, makes them the go-to choice for flexible and rigid-flex circuit boards. This property becomes especially advantageous in high mobility applications where the PCB undergoes regular utilization.
● Improved Functionality: Exhibiting superb performance for both single layer and multilayer circuits, Kapton PCB make an excellent option for a variety of electronic applications. Single-sided and double-sided Kapton PCB boast high reliability and efficiency across diverse utilizations.
● Excellent Heat Resistance: Kapton PCB offer excellent heat resistance that does not compromise the electric properties of the board. They outperform FR4 PCB in terms of thermal cycling and heat dispersion, proving their reliability under severe thermal situations.
● High Resistance to Chemical Damage: With better resistance to hydrocarbons and greases as compared to FR4 PCB, Kapton PCB makes an excellent selection for military, aerospace, and other harsh environmental conditions.
● High Durability: Kapton PCB, owing to their high durability, withstand extreme thermal conditions and vibrations, making them a trustworthy choice for different electronic applications.
● Efficient in Integration Applications: Kapton PCB are modifiable to suitable forms, make them suitable for integration applications, where FR4 PCB may not be as well-suited.
To sum up, the singular attributes of Kapton PCB including exceptional tensile strength, flexibility, extraordinary heat resistance, superior resistance to chemicals, and remarkable durability make them a preferable choice over FR-4 PCB for a diverse range of electronic applications.
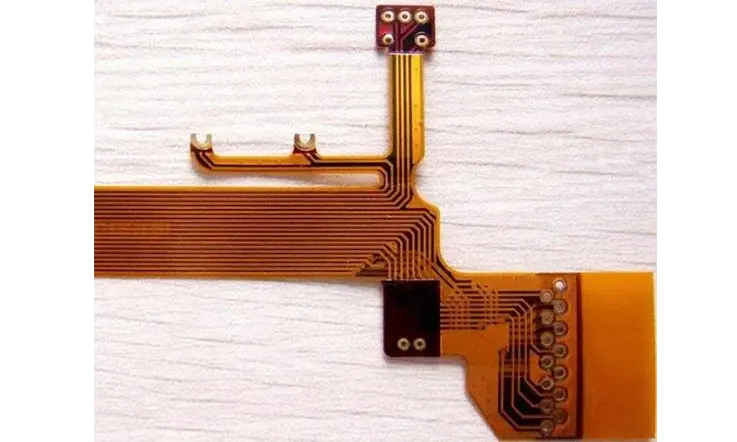
Challenges of Using Kapton PCB
While Kapton PCB offer many benefits, they also present some challenges compared to traditional FR-4 PCB. Here are a few challenges associated with using Kapton PCB:
● Cost: Kapton PCB are more expensive to manufacture than FR-4 PCB due to the specialized equipment and materials that are required. This can make them a less attractive option for cost-sensitive applications.
● Flexibility: On the one hand, the flexibility of Kapton PCB underscores a core benefit; on the other hand, it can trigger complexities during fabrication, handling and component installation. The flexibility of the base substrate could potentially interfere with component alignment and assembly, thus necessitating supplementary support mechanisms.
● Mechanical Stability: The propensity of Kapton PCB towards mechanical damage, in comparison to FR-4 PCB, is not to be ignored, especially under circumstances of continued bending or twisting. This can affect the reliability of the circuit and can lead to failures over time.
● Surface Finish: While Kapton PCB are often coated with a thin layer of metal to protect the copper traces. However, due to the flexibility and thinness of the Kapton substrate, the surface finish might pose more challenges compared to that of an FR-4 PCB.
● Electrical Insulation Properties: Although Kapton exhibits commendable electrical insulation capabilities, its not suitability for high-frequency applications due to its relatively lower dielectric constant in contrast with conventional PCB materials.
Conclusion
Kapton PCB are a distinct genre of printed circuit board, utilizing a flexible and heat-resistant Kapton film as its foundation. These PCB proffer an array of benefits compared to the conventional FR-4 PCB, encompassing flexibility, high thermal endurance, and robustness, rendering them an optimal choice for a wide range of applications across industry verticals such as aerospace, healthcare, automotive, consumer electronics and industrial Device.
Nonetheless, Kapton PCB can also present challenges such as cost, mechanical stability, surface finish, component mounting, and electrical insulation properties A balanced evaluation of these pros and cons is required when selecting Kapton PCB, to ascertain whether they align with the particular requisites of a given application. Summarily, Kapton PCB represent a path-breaking material that initiates fresh opportunities in electronics design, notably in instances necessitating high thermal resilience and flexibility.
Related Posts:
1. Oshpark PCBs for Optimal Solutions
2. Battery FPC: Advantages, Limitations, Application and Future Developments
3. FPC Circuit Board Materials and Application
4. What Is the Main Differences Between FFC and FPC?
5. Flex PCB
