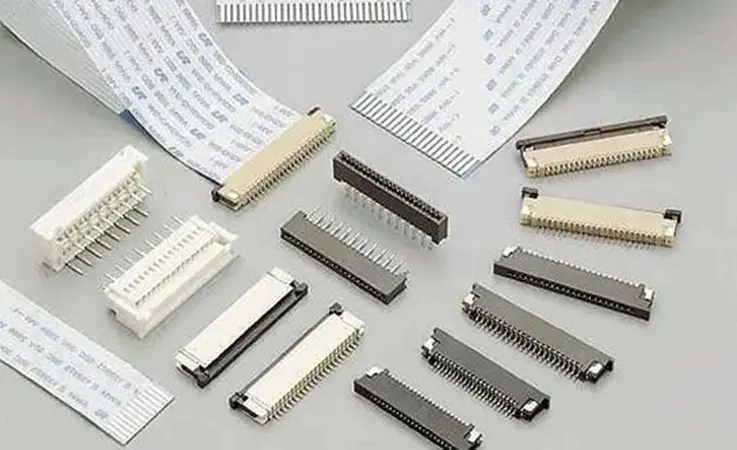

As a response to the trend toward miniaturization in the electronics industry, Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) connectors have been designed to meet the demands of this expanding market, which require smaller centerlines or pitch spacing, lower profile heights, and lighter interconnects. JarnisTech, being a trusted manufacturer of FPC products, offers dependable interconnects that incorporate an actuator mechanism to secure the cable termination. Our FPC solutions are also field-terminatable with no special tooling required.
Available in centerline spacings of 0.25mm, 0.3mm, 0.5mm, 1.0mm and 1.25mm, and our connectors are engineered with low profile heights and lightweight. These specifications have been specifically crafted to cater to modern electronic devices, with a distinct focus on fulfilling their predilection for miniaturization.
Flexible Connector Types: FFC Connector and FPC Connector
In response to the burgeoning market for compact electronic devices, manufacturers have developed connectors that offer shorter centerlines or pitch distances, lower profile heights, and lighter interconnect solutions. Various techniques can be utilized to evaluate the capabilities of Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) connectors.
FPC connectors are becoming increasingly popular as cable connectors for smart applications due to their delicate shape factors and exceptional flexibility. These connectors offer high density and can serve a wide range of advanced applications and market segments. With superior profile design and a constant decrease in form factor standards, FPC connectors provide flexible cable solutions that can be incorporated into even the smallest of spaces.
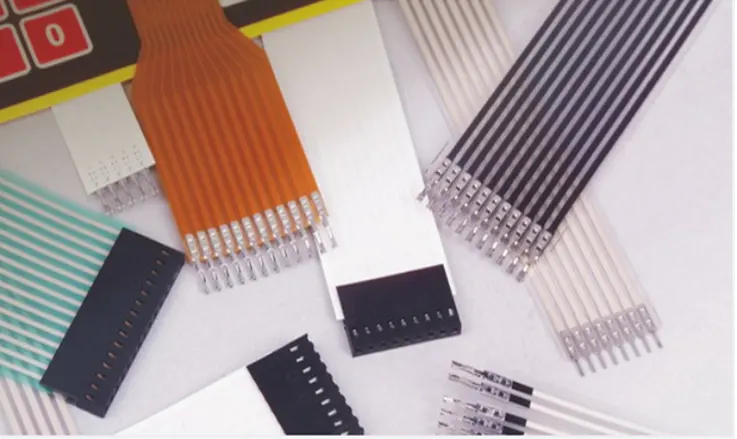

● Flexible Flat Cable FFC Connector
Flexible Flat Cable (FFC) connectors are commonly utilized in cable-to-board applications for connecting ribbon-type FFC to PCB electronics. With their high-density and ultra-thin form factors, these connectors seamlessly fit into space-restrictive and compact areas. Their application is indeed quite pervasive, extending to consumer electronics including computers, digital cameras, peripheral devices, household appliances and telecommunication devices like phones. These connectors are cleverly housed within flexible casings composed of plastic, polymer, specialized rubber, or film which encompass a built-in metal connector in single or double-row configurations. The connectors also come with a range of locking styles to choose from, catering to the specific needs of the application.
Where Can FFC Be Used?
Flexible Flat Cables (FFC) are a variety of ribbon cable with a centralized structure. They have smooth connectors that do not require any special tools for installation. Typically, FFC cables comprise a plastic film with a series of metallic connectors known as “pitch.”
FFC cables occupy less space, are more flexible than round cables, and frequently offer greater EMI/RFI removal, along with the elimination of wire coupling issues. They are preferred in sophisticated electrical systems, especially when high flexibility is demanded, such as connections to a moving printer head, mobile phone wrapping, or situations with mass or space constraints.
In the electronic equipment market, a wide array of FFC cables is available for soldering and connecting with pitches of 0.5mm, 0.8mm, 1mm, 1.25mm and 2.54mm. At JarnisTech, offering a comprehensive collection of FFC connectors manufacturing to accommodate a multitude of pitch specifications to cater to their varied requirements.
● Flexible Printed Cable (FPC Connector)
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) connectors carry out the function of delivering connection between the board and the Flexible Printed Cable (FPC) – a specific type of Flexible Flat Cable (FFC) that differentiates itself with its conductors neatly printed rather than being embedded within the cable substrate. In the industry, these connectors often go by the alias of ribbon connectors.
Types of FPC Connectors
In the realm of Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) items, a variety of FPC connectors cater to purposes. Internal FPC connectors stand out as an employed choice, in the sector.
● 0.5mm pitch: Y5B series.
● Pitch of 0.2mm: Y2B series.
● Y3BL Series and Y3B/W Series have 0.3mm pitch.
Where Can FPC Be Used?
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) connectors are extensively utilized in a wide range of significant and convenient applications, including wearable electronics and medical devices. The increasing use of Flexible Flat Cable (FFC)/FPC connectors in the automotive industry offers innovative features such as in-vehicle infotainment, bright lighting, driving autopilot modes like ADAS, and support for navigation and safety settings.
With the implementation of smart manufacturing and 5G technologies, FFC/FPC connections are exploring opportunities in a variety of next-generation applications. Our company, Jarnistech, offers high-performance, versatile, and dependable FPC solutions to cater to the needs of all emerging devices.
Micro flex connections with 1.00mm pitch and 0.50mm pitch are commonly employed in automotive, medical, communication, data, and commercial systems. Our ClincherTM and DuflexTM connectors are ideal for industrial and modulation applications where shock or vibration is a concern, such as industrial control systems, non-automotive transportation, and retail items.
Designers are fond of FFC/FPC connectors as they offer greater flexibility than standard rigid circuit boards when combined with flexible cable.
FPC Board Types
The present-day market is well-stocked with a wide range of distinct flexible circuit board, each intentionally crafted to cater to diverse requirements, technical specifications, and applications. As engineers within the PCB domain, acquiring knowledge on the multiplicity of flexible circuit boards on offer becomes a necessity. This understanding aids in the decision-making process when needing to identify a suitable PCB circuit board for specific project needs.
Flexible printed circuit boards have many types, which encompasses Single-Layer Flex, Double-Sided Flex and Multi layer Flex. Each type is intricately designed to cater to specific needs as well as applications.
● Single-Layer Flex, being the most economical solution, comprises a polyimide or polymer dielectric conductor layer with metal on one side. It includes a polyimide cover to provide insulation and add to the board’s safety.
● Double-Sided Flex features two conductor layers on each dielectric layer, joined together via copper-plated holes. This type of flexible circuit offers greater design flexibility and is more cost-effective than multi layer flex.
● Multi layer Flex is designed with multiple conductor layers and comes in a variety of shapes and sizes. However, these types of FPC are more expensive to manufacture than single and double-layer flexible circuits, and hence are only utilized in applications that require more complex circuits.
What is the Difference Between FFC and FPC?
Despite having a similar appearance, flatness, and data transmission capabilities, FFC and FPC are two different entities which are often confused.
● FFC typically consist of straight-through conductors, and their pinouts are either 1 to1 or 1-n. In contrast, FPC possess multiple-layered conductors that cross over one another, enabling them to have a wide variety of pinouts. Due to their impedance adjustment capability, FPC are preferred for data cables like LVDS. Besides being rectangular, FPC can also be designed with distinct bends and angles.
● The selection between an FFC and an FPC greatly depends on the intended application. As flex PCB layout designers, we are well-equipped to assess your particular requirements and guide you in selecting the optimal cable type.
Application Distinctions of FFC and FPC
● Within the realm of electronics, all-encompassing applications are observed for both FFC and FPC cables. Notably in high-flex applications, FFC cables have become indispensable components across various contemporary electronic devices. These cables extend their functionality to an extensive range of electronic apparatus such as copiers, plotters, scanners, fax machines, auditory systems, LCD appliances and beyond.
● By comparison, FPC cables can be found in a diverse range of electronic devices, including antennas, audio devices, LCD TVs, cameras, laptops, printers, and aviation equipment. These cables have seen considerable enhancements with respect to performance and quality over time, thereby reaffirming their remarkable suitability across an impressive range of applications within the electronics sphere.
Differences in Manufacturing Between FFC and FPC
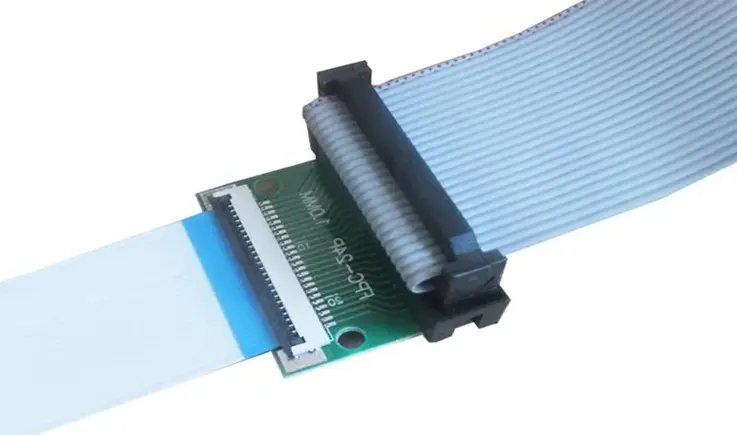
● Manufacturing: The manufacturing process of flexible flat wires differs significantly from that of flexible printed circuits. Flexible flat cables need to be coated with polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and possess flat copper wires. Furthermore, two-layered wires lay the foil over the copper conductor. Comparatively, FPC are produced by etching Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL), followed by coating multiple layers.
As a result of this approach, FFC tend to be thicker than flexible printed circuits.
● Thickness: FFC, in comparison to flexible printed circuits, are aptly qualified for diverse applications, especially in tight spaces that demand thicker cables. In scenarios marked by intense environmental conditions, FFC wires typically range from a thickness of 0.5mm to 2.54mm, thus providing a heightened sense of durability and trustworthiness. Conversely, FPCs are characterized by thickness measurements ranging from 0.15mm to 0.2mm, making them a more spatially efficient alternative.
● Wiring: The wiring properties of FFC and FPC play a crucial role in enabling the transmission of data between different locations within an electronic device.
FFC wiring involves determining the optimal wire quantity and spacing for the intended application, including motherboards and mechanical components. This process helps to reduce production costs and the size of electronic gadgets while improving manufacturing efficiency.
In contrast, FPC wiring involves either etching a copper circuit or putting a thick polymer layer on the substrate. This wiring method is ideal for designing compact, thin, and lightweight electronics that require a one-sided circuit design or a multi layer 3D PCB. Using FPC wiring results in a 70% reduction in the volume and weight of the wiring installation compared to standard procedures. Furthermore, the increased strength of the supported parts contributes to improved stability. This wiring technique enables data communication between a PC’s hard disk and the main board.
● Unable to Replace One Another: In conclusion, FPC and FFC cannot be interchanged when it comes to connectivity and functionality because of their differing manufacturing processes. Additionally, their production strategies are classified, further complicating the possibility of substituting one for the other.
Flexible printed circuits are comparatively susceptible to external factors, whereas flexible flat cables feature excellent heat conductive materials, making both cable types suited for specific use cases.
Therefore, it is essential to evaluate the intended application thoroughly and determine which type of cable is best suited for the specific project’s requirements.
Different Connector Types of FPC and FFC
Among the most recurrently employed types of FFC and FPC connectors, one can identify Low Insertion Force (LIF) and Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) as predominant options.
● LIF connectors represent a cost-beneficial and dependable solution, necessitating a gentle application of force for insertion into the slot. Their lower endurance. However, they have a shorter lifespan of up to 10 mating cycles, making them less durable than ZIF.
● Contrasting this, ZIF connectors present a more extended lifespan with up to 30 mating cycles catered for both flexible flat cables and flexible printed circuits. They also feature a mechanical slider that clicks into place above the cable after it is pressed into the insulator slot, providing additional stability and security.
Cost Comparison of FFC and FPC
When weighing costs between FFC and FPC, multiple facets warrant consideration. FFC predominantly appear to be economically efficient compared to FPC owing to their less complicated fabrication process, decreased material utilization, and less intricate design. Nonetheless, in the context of intricate or high-density circuits, FPC might proffer superior cost efficiency due to their elevated circuit density and the capability to diminish the overall size of the electronic gadget, thereby curtailing materials and assembly expenditures.
Indeed, the specific demands of the application must be considered while scrutinizing the cost of every option. For instance, in scenarios that necessitate superior flexibility, an FFC could be the preferable choice, disregarding the increased cost. Analogously, if the application demands higher density or more complex circuitry, FPC might turn out to be the prime selection even with the elevated production expenses.
In the end, the cost juxtaposition between FFC and FPC is contingent on the unique demands of every project. Collaborating with a manufacturer to scrutinize these requirements and balance the advantages and expenditure of each alternative could assist in discerning the most fiscally efficient solution for the given project.

Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between FFC and FPC for a specific application hinges largely on the particular needs of said application. Fundamentally, FFC are apt for straightforward interconnection solutions where flexibility is deemed vital, whereas FPC are more fitting for crafting intricate and denser circuits. This choice mandates the consideration of numerous variables, encompassing cost, adaptability, spatial limitations, signal velocity, and noise, as well as the milieu where the cables will be deployed.
Therefore, as a manufacturer of both Flex and Rigid PCB, JarnisTech recommends that our clients consult with their PCB design engineers or contact our manufacturing team to determine the best option that suits their individual requirements. Our team of experts can provide professional guidance and recommend the most appropriate solution based on our clients’ specific needs.
We recognize that a multitude of elements require contemplation, such as cost, flexibility, spatial confines, signal speed, noise, and the targeted operational environment. Our commitment is to ascertain that our clients procure the most optimal product tailored to meet their precise requisites.
Summary
The performance of FFC and FPC is influenced by some fundamental distinctions between the two. Each type enables diverse wiring layouts for specific purposes, such as connecting a hard disk to the motherboard for data transfer. Adequate space is required for the optimal functionality of both cable types in their respective settings. Additionally, differences in measured thickness should be considered to ensure the cables are used and fitted advantageously.
Should you have any inquiries or challenges regarding FFC and FPC, we encourage you to connect with us. Our team of expert PCB engineers is on standby, and to address your questions and steer you through any complications you may encounter.
Related Posts:
1. Oshpark PCBs for Optimal Solutions
2. Battery FPC: Advantages, Limitations, Application and Future Developments
3. FPC Circuit Board Materials and Application
4. Flex PCB
5. Understanding Kapton PCB: Advantages, Challenges, and Applications
