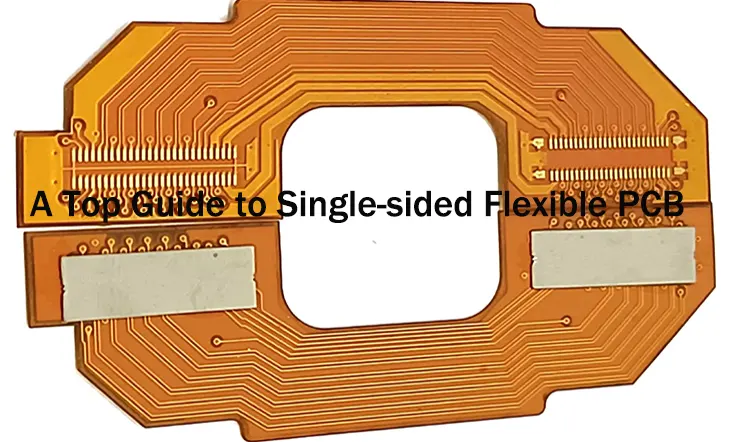
A flexible printed circuit board (FPC) is a highly reliable and high-performance printed circuit board that employs polyimide or polyester film as its base material. Often referred to as a soft board or FPC, it is widely used for its low weight and slim profile, which enable easy bending, folding, coiling, and even extension in three dimensions. This technology is known for its ability to achieve lightweight, miniaturization, and thinness, facilitating the integration of components and wire connections.
Because of the unique properties of the FPC soft plate, such as its light weight, slim profile, and irregular shape, traditional molding techniques are impractical. Additionally, lasers are not suitable for mass production due to their low efficiency. Therefore, in order to achieve efficient mass production, die punching (die cutting) is the only viable method available.
Die punching is a process where a shaped die is used to cut the flexible PCB to the desired shape and size. This method offers high precision, accuracy, and efficiency in cutting, making it a popular choice for flexible PCB manufacturing. In this article, we will explore the different die punching methods used in the manufacture of flexible PCBs, their advantages and disadvantages and best practices for die punching.
Overview of Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs, also known as flex circuits or FPCs, are printed circuit boards that are designed to be flexible. They are made of thin, flexible substrates such as polyimide or polyester that can bend and conform to irregular surfaces or tight spaces.
Flexible PCBs offer several advantages over traditional rigid PCBs, such as weight and space savings, increased durability, and greater design flexibility. They can also enable the creation of more compact and lightweight devices, which is crucial in industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive.
Flexible PCBs can be made using a variety of manufacturing processes, including etching, laminating, and additive printing. They may also incorporate additional features such as flexible solder masks and coverlays, embedded components, and advanced interconnect technologies.
Applications for flexible PCBs are numerous and varied, including in consumer electronics, medical devices, aerospace and defense, and automotive industries. Overall, the use of flexible PCBs continues to grow as the demand for advanced and miniaturized electronic devices increases.
What Is flexible PCB Die Punching ?
Flexible PCB die punching is the process of cutting flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) into a specific shape and size using a die and a punching tool. The PCBs are made of thin, flexible material that can bend and twist, making it challenging to cut accurately. Die punching involves the use of a die, which is a thin piece of metal that has a cutout of the desired shape of the PCB, and a punching tool, which is used to push the material through the die, cutting it to the desired size and shape. This process is crucial for producing flexible PCBs that meet the exact specifications required for various electronic applications.
Die Punching Process for Flexible PCBs
Here are the steps involved in the die punching process for flexible PCBs:
● Design the PCB: The PCB design software is used to create the desired PCB layout and design.
● Fabricate the PCB: The flexible PCB is fabricated using a manufacturing process that involves patterning and etching of the conductor and dielectric layers.
● Prepare the die punching equipment: The steel rule or rotary die and punching tool are chosen, set up, and calibrated for the PCB design specifications.
● Align and fix the PCB: The PCB is accurately aligned and fixed onto the punching surface to prevent any movement during the cutting process.
● Position the die and punching tool: The die is placed onto the punching surface, and the punching tool is positioned to ensure accurate cutting of the PCB.
● Initiate the cutting process: The punching tool is activated to push the PCB through the die, precisely cutting the material to the desired shape and size.
● Inspect the cut PCB: The cut PCB is visually inspected to ensure that it has been cut accurately and there are no defects or deviations.
● Repeat the process: The above steps are repeated for each PCB until the manufacturing batch is complete.
Advantages of Die Punching for Flexible PCBs
Die punching is a common and cost-effective manufacturing method for producing custom-shaped flexible PCBs, and it offers several advantages over other methods. Some of these advantages include:
● Precise accuracy: Die punching provides high precision and accuracy in creating custom shapes and sizes, allowing for tight tolerances and exact specifications.
● Cost-effective: Die punching is a relatively low cost process that utilizes customized metal dies and can produce large quantities of identical parts quickly and efficiently.
● Scalable: The die punching process is highly scalable, making it an excellent option for large-scale production with fast turnaround times.
● Minimal material waste: Due to the nature of die punching, there is minimal material waste, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
● Improved product quality: The precise and consistent cutting of die punching creates cleaner edges, which can improve the overall quality and performance of flexible PCBs.
● Design flexibility: Die punching offers greater design flexibility to produce a range of shapes and sizes, including intricate or complex designs that may not be possible with other manufacturing methods.
Types of Die Punching Methods for Flexible PCBs ?
There are several methods for die punching flexible PCBs, including:
● Steel rule die cutting: This method uses a die made of steel rule blades, mounted on a wooden board, to cut the flexible PCB.
● Rotary die cutting: This method uses a cylindrical die to cut the flexible PCB as it passes through a press.
● Laser cutting: This method uses a high-powered laser to cut the flexible PCB along a pre-determined path.
● Waterjet cutting: This method uses a high-pressure stream of water to cut through the flexible PCB.
● Punch and die cutting: This method uses a hydraulic press with a punch and die set to cut the flexible PCB to the required shape.
Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the type and thickness of the PCB material, the desired level of precision, and production speed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Various Die punching Methods
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of various die punching methods for flexible PCB manufacturing:
Steel rule die cutting
Advantages:
● Simple, versatile and cost-effective method.
● Ideal for low-volume and short-run production.
● Can handle various PCB materials and thicknesses.
Disadvantages:
● Limited precision for cutting intricate shapes, and can cause rough edges.
● Not suitable for larger volume productions.
Rotary die-cutting
Advantages:
● High-speed and high-volume production capacity.
● Can handle intricate shapes and produce precise cuts.
● Can cut multiple layers of material in a single pass.
Disadvantages:
● Expensive equipment and tooling, and longer setup times.
● Can only handle specific shapes and sizes.
Laser Cutting
Advantages:
● High precision and accuracy for intricate and complex shapes.
● Capable of cutting thinner and more delicate materials without causing stress or distortion.
● Minimal waste production and consistent laser power.
Disadvantages:
● Higher equipment and maintenance costs.
● Limited cutting speed, especially for thicker material.
Waterjet Cutting
Advantages:
● Can cut almost any material with high precision, including thicker materials.
● No heat-affected zones, no material distortion.
● Minimal tool wear and easy to maintain.
Disadvantages:
● Limited to straight-edged cuts due to the nature of the process.
● Slower compared to other cutting methods such as laser or die-cutting.
Punch and Die Cutting
Advantages:
● High-speed cutting process with low setup time.
● Consistent, precise and efficient cuts with low tooling costs.
● Ideal for lower-volume productions.
Disadvantages:
● Not suitable for cutting intricate shapes
● Limited cutting size and material thickness capabilities
When choosing a die punching method for flexible PCBs, it is essential to consider the material properties, production volume, production speed, precision, design complexity, and equipment cost to determine the most suitable method.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a Die Punching Method for Flexible PCBs
When choosing a die punching method for flexible PCBs, some of the key factors to consider are:
● The type and thickness of the PCB material
● The desired level of precision and accuracy in the cutting process
● The production speed required
● The complexity of the PCB design
● The cost of the punching method and equipment
● The flexibility of the method to handle different PCB shapes and sizes
● The complexity and frequency of changeovers between different PCB designs
● The environmental impact of the method, such as waste generation and energy consumption.
Considering these factors helps select the most suitable die punching method for manufacturing flexible PCBs that meet the desired quality standards, production efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Why Flexibel PCB Profiling Need Die Punching ?
● Flex and rigid-flex PCB profiling processes are typically associated with techniques such as V-scoring, milling/ routing, and laser cutting. However, an additional method worth considering is die punching. This term is commonly used within the PCB industry to describe punching fixtures.
● While V-scoring, milling, and laser cutting are all viable processes for the profiling of rigid materials, they are not ideal for cutting thin and flexible materials. In the case of high-volume production, the fabrication of FPC can be completed more cost-effectively and quickly using the traditional method of punching.
● Punching is a widely used process for cutting thin and flexible materials such as FCCL, coverlay, EMI film, PSA, stiffeners, and more in the production of flex circuits. During the flex PCB punching process, the individual components are punched in accordance with the profile on the production panel, resulting in either unit components that have been separated from the panel or the panel left with small connection tabs.
●To carry out the punching procedure, a punching machine and a custom set of punching dies are required. Each die is made up of two sections; the first contains sharp blades, while the second provides support. Compared to laser cutting, punching capacity for cutting and profiling FPC materials is typically greater, resulting in lower costs.
● Punching dies need to be created based on the Gerber files of the production panel, with the cost of the dies considered a one-time, non-recurring engineering cost (NRE cost). This implies that payment is required only once, and no additional fees will be levied even for future repeat orders until the end of the dies’ useful life.
Therefore, it is important to understand the die punching procedure and its advantages, particularly for high-volume production of flex circuits and related parts. With its affordability and efficiency, die punching offers clear benefits over other, more expensive and time-consuming methods.
In a word, Die punching is a crucial step in the flexible PCB manufacturing process as it allows for the precise and efficient cutting of the flexible PCBs to their desired shape and size. Flexible PCBs are used in various industries, including medical, automotive, and aerospace, where size, weight, and flexibility are essential factors. The die punching process enables the production of highly intricate and complex flexible PCB designs that meet the stringent requirements of today’s advanced electronics.
Key Considerations for Flexible PCB Die Punching
There are several key considerations that manufacturers must take into account when using die punching for flexible PCBs:
● Material selection: Choose a flexible PCB material that is compatible with the specific die punching process and commercial equipment being used.
● Design for manufacturability: Ensure that the flexible PCB design takes into account the tooling and die specifications for die punching, including considerations such as part density, panelization, and material thickness.
● Tooling design: Develop custom tooling that is optimized for the specific flexible PCB design and die punching process, taking into account factors such as tool size and shape, blade angle, and die clearance.
● Material handling: Proper handling of the flexible PCB material before, during, and after die punching is crucial to ensure that the material remains flat and consistent.
● Quality control: Implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure that the final punched flexible PCBs meet the required standards for size, shape, and functionality.
● Process monitoring and optimization: Regularly monitor and optimize the die punching process to ensure that it remains efficient and effective, and to identify potential issues or opportunities for further improvement.
By taking into account these key considerations, manufacturers can optimize the die punching process for flexible PCBs and reduce the risk of defects or manufacturing errors.
Comparison with Other PCB Punching Techniques
There are several techniques for punching or cutting PCBs, each with its own advantages and disadvantages when compared to die punching for flexible PCBs. Some of the commonly used alternatives include:
● Laser cutting: Laser cutting uses a laser beam to cut through the PCB material, providing high accuracy and precision, but it can be more expensive and may not be suitable for all materials, especially highly flexible ones.
● Waterjet cutting: Waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water to cut through the PCB material, which can be useful for cutting thick or hard materials but can result in lower precision and accuracy.
● V-scoring: V-scoring involves creating a groove in the PCB material that can be easily broken later to separate the PCB. This technique is cost-effective and suitable for rigid PCBs, but may not be ideal for flexible PCBs.
● Routing: Routing uses a rotating tool to cut through the PCB material, providing more flexibility than die punching but may result in rougher edges and longer processing times.
As a FPC design enginners, as we know that die punching for flexible PCBs offers a cost-effective and scalable solution that provides precise, accurate and clean cuts with fast turnaround times. While other techniques may have their own advantages, die punching remains a popular and effective option for many manufacturers.
Application of Flexible PCB Die Punching in Industry
Flexible PCB die punching is being widely used in various industries, especially for manufacturing electronic devices where space and weight are limited, and intricate, custom shapes are required.
Some examples of industries that utilize flexible PCB die punching include:
● Consumer electronics: Flexible PCBs are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, wearables, and other portable devices, where space constraints and lightweight designs are paramount.
● Medical devices: Medical devices require flexible PCBs to conform to the contours of the human body and incorporate multi-layer functionalities. Die punching can produce custom shapes for these components while maintaining accuracy and consistency.
● Aerospace and defense: Flexible PCBs are used in the aerospace and defense industries, where weight reduction and tight packaging are essential due to the limited space available in aviation or military equipment.
● Automotive: Die punching is used in the automotive industry to create flexible PCBs for a wide range of components, including sensors, lighting, infotainment systems, and more.
Flexible PCB die punching is also used in other applications, such as LED lighting, industrial equipment and control systems, and renewable energy systems. Overall, the flexibility and accuracy of PCB die punching make it a crucial technology for producing complex electronic devices that are lightweight, durable, and precise.
Why Choose JarnisTech ?
As a leading FPC and FR4 PCB manufacturer in China, we are highly regarded for our commitment to providing our customers with the highest quality circuit boards. Our production process employs state-of-the-art, high precision die punching equipment, which allows us to meet the demands for high precision and quality FPC circuit boards.
Our advanced die punching equipment is a key factor in producing FPC circuit boards that meet and exceed our customers’ expectations. By utilizing high-precision technology, we are able to ensure that our products are accurate, reliable, and of the highest quality. Additionally, we have earned the trust of our clients through our consistent delivery of exceptional results.
We are dedicated to leveraging cutting-edge technology in order to remain at the forefront of the PCB manufacturing industry. By investing in advanced equipment and emphasizing high-quality production standards, we have earned a reputation as a leading provider of both FPC and FR4 PCB solutions. Our commitment to delivering unparalleled customer satisfaction is a central aspect of our business philosophy, and we are proud to have earned the trust and loyalty of our clients.
Our Flex PCB Board Die Punching Capability
● Material of punching: flexible printed circuit board;
● Machining Accuracy: up to +-0.002mm;
● Punching material thickness: 0.13mm;
● Tolerance: up to +-0.02mm;
● Die steel: D2(AISI), SKD11 (JIS) etc;
● Use wire EDM & CNC machining centers to construct die components.
● Precision measuring instruments: 3D CMM,Digital projector, microscope, etc.
● Export FPC Circuit boards to: USA, UK, Canada, Malaysia, Mexic, etc.
● Minimum order: Minimum order quantity
● Lead time: 2-7 days;
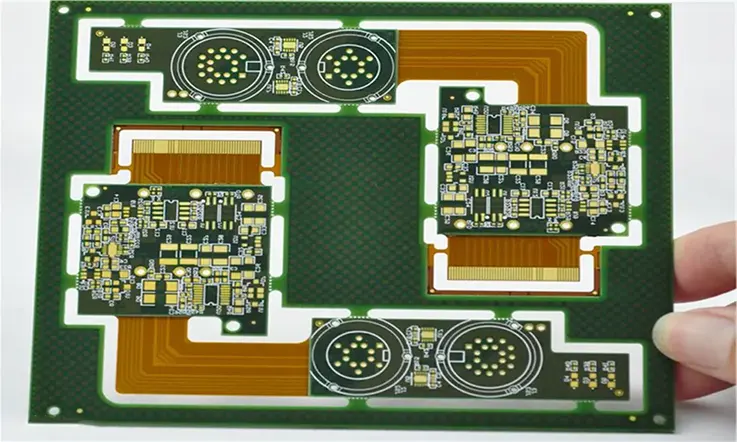
Flexible PCB Boards Punching Common Problem
Like any manufacturing process, punching in flex PCB production can lead to issues that need to be addressed to ensure high-quality end products. The following are some common problems that can occur during the flexible PCB punching process:
● Burrs and Frayed Edges: Excessive punching pressure or an inadequately sharpened blade could cause the edges of the FPC to become rough or frayed, resulting in poor appearance and reduced conductivity.
● Misalignment: Punching dies need to be aligned with the FPC to ensure accurate punching of the profile. Any dies that are out of alignment will result in a poorly cut FPC that may need to be reworked or discarded.
● Inaccurate Board Dimensions: If the punching dies are improperly calibrated, the resulting FPCs may not be the correct size or shape, which could adversely affect the function of the product.
● Distorted Shape: The FPC may be deformed or distorted if excessive force is applied during the punching process or if the FPC is not held securely in place.
To avoid these issues, it is important to properly calibrate the punching machine and regularly sharpen and maintain the punching die blades. The punching pressure should be adjusted to optimize the cutting process while minimizing damage to the FPC.
Additionally, frequent checks for accurate alignments and dimensions can help identify and address problems before they become more significant. By monitoring and addressing these common issues, punching a flexible PCB can result in high-quality and reliable end products.
Future Developments and Trends in Flexible PCB Die Punching
Flexible PCB die punching technology is continuously evolving to meet the demands of the electronics industry and to take advantage of advances in materials, equipment, and automation. Some potential future developments and trends in flexible PCB die punching includes:
● Advanced materials and substrates: As flexible PCB materials become more diverse and sophisticated, die punching technology will need to adapt to handle the challenges of thinner and more delicate substrates, such as polyimide and other advanced films.
● Miniaturization: With the increasing demand for smaller and lighter electronic devices, die punching technology will need to enable the creation of smaller and more intricate shapes with even higher precision and accuracy.
● Automation: To increase throughput and efficiency, die punching manufacturers will continue to adopt automation techniques such as robotic part handling, integrated quality control, and real-time process monitoring and optimization.
● Innovative tooling and techniques: Some manufacturers are exploring the use of new tooling designs such as diamond tooling for cutting and shaping flexible PCBs and non-contact methods such as plasma cutting.
● Environmental and sustainability issues: Die punching manufacturers are looking for ways to reduce the waste generated during the punching process and to adopt more sustainable materials and processes to support the circular economy.
So, flexible PCB die punching technology is likely to continue evolving and playing a critical role in the development of the next generation of electronic devices. The focus will be on delivering higher precision, speed, and automation to meet the increasing demands for smaller, lighter, and more powerful components.
Final Words
As a renowned PCB manufacturing and assembly company based in China, we have amassed an extensive 20-year experience in the field of printed circuit boards. With our comprehensive expertise, we are able to provide custom solutions to customers worldwide, including Fastening Bases of Mould that are tailored to their specific press machine and requirements.
Our highly skilled and experienced engineers use cutting-edge equipment and modern manufacturing facilities to craft each printed circuit boards with precision and efficiency. Additionally, we have established a state-of-the-art quality assurance and management system that ensures all of our rigid, flex, and rigid-flex printed circuit boards consistently meet the highest standards of quality and are readily accepted by our customers.
At JarnisTech, we are committed to delivering the best possible results and exceeding our clients’ expectations. To learn more about our capabilities and how we can help with your next PCB project, please contact us at [email protected]. Our team will be happy to discuss your specific requirements and provide you with the necessary information.