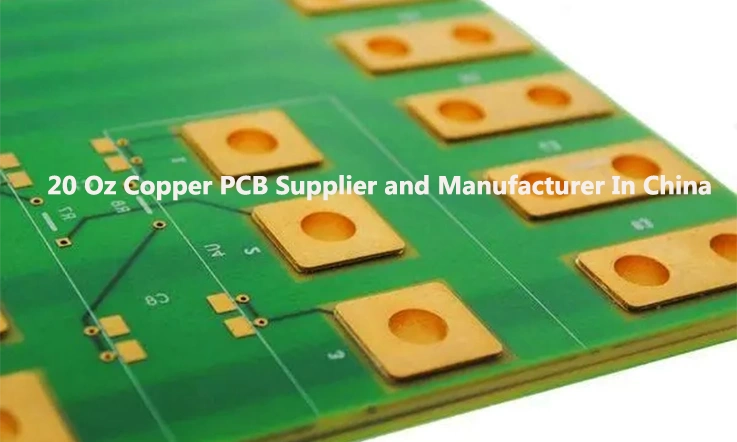
With the increasing power densities observed in advanced electronics, there is a growing trend towards adopting thicker copper PCB boards that surpass 10 oz. Achieving exceptional performance necessitates the use of 20 oz copper PCB, which boast an extreme foil thickness of 700 μm (0.7 mm).
Nonetheless, the process of reliably manufacturing multilayer PCB with 20 oz copper poses significant fabrication challenges. In this article, we delve into the advantages offered by 20 oz copper boards, the exacting manufacturing capabilities they demand, potential applications for this cutting-edge PCB technology, as well as key considerations to bear in mind when implementing it.
What is a 20 oz Extreme PCB?
The thickness of copper on a PCB is typically measured in ounces per foot (oz/ft2) indicating the weight of the copper foil, in a one square foot section of the board excluding the dielectric base. Common copper weights include 1 oz (35 μm) 2 oz (70 μm) 10 oz (350 μm), 14oz and 20 oz (700μm) options.
A 20 oz PCB refers to a printed circuit board with a layer of 20 ounce copper thickness. Such PCB can withstand significant thermal proportions and are engineered to cope with ample current quantities. How might one measure the thickness of a 20 oz PCB? Conventionally, a 1 oz PCB exhibits a thickness of 1.37 mils or 0.00137 inches. Consequently, a metal core PCB omprised of a 20 oz copper layer, would possess a thickness equal to 20 times 1.37 mils, equating to roughly 27.4 mils or 0.0274 inches.
Essentially, a 20 oz copper PCB contains 20 ounces of copper foil per square foot on each metal layer. In terms of thickness, 20 oz copper translates to approximately 700 μm (0.7 mm) or 28 mils. This substantial foil thickness allows for exceptional power handling and enhances overall reliability capabilities.
Benefits of 20 oz Copper PCB
The utilization of 20 oz copper PCB technology offers several significant advantages, including:
Highest current capacity: The substantial copper cross-section enables 20 oz copper PCB to handle extremely high current loads without overheating, ensuring reliable performance.
Lowest losses: With minimal resistive losses, these PCB facilitate highly efficient power transfer and conversion, reducing energy wastage.
Finest thermal performance: The thick copper layers act as effective heat spreaders, efficiently dissipating heat and contributing to optimal component temperature management.
Superior shielding: 20 oz copper PCB feature thick and uninterrupted copper planes that provide exceptional electromagnetic interference (EMI) isolation, ensuring reliable signal integrity.
Extreme reliability: These PCB exhibit high resistance to challenges such as thermal cycling, electromigration, and physical stresses over prolonged periods, enhancing overall reliability and longevity.
Low voltage drop: The minimal resistivity of the thick copper enables negligible voltage loss along power distribution paths, ensuring proper power delivery.
High power density: 20 oz copper PCB offer the maximum power delivery potential within a given PCB footprint, making them suitable for applications requiring high power densities.
Component integration: The presence of 20 oz copper inner planes allows for the embedding of heavy power components, facilitating efficient and compact PCB designs.
The utilization of 20 oz copper represents the forefront of PCB material technology, meeting the demands of extreme electrical and thermal requirements in various applications.
Design Process of the 20 oz PCB
Before proceeding with the design of a 20 oz PCB, it’s imperative to deliberate on specific parameters including spacing, optimal dimensions, and types of components. These integral factors will direct the subsequent stages of your design process.
Pay attention to copper fill levels in the inner layers to prevent excessively low resin levels. Insufficient resin can lead to voids between the board’s layers, potentially causing delamination.
Utilize software tools to assist in determining the types and quantities of prepregs required for achieving multilayer designs effectively.
Give due consideration to the galvanic coating aspect. Working with 20 oz PCB necessitates the use of more galvanic copper compared to other copper thicknesses.
Ensure the layers of solder resist are applied with adequate thickness. This will provide sufficient protection for the mosaic edges on the PCB. For example, the end circumferential thickness should be at least 0.25mm thicker than the initial thickness.
By factoring in these considerations and taking the necessary precautions during the design process, you can ensure optimal performance and reliability of your 20 oz PCB.
Manufacturing Challenges with 20 oz Copper
The fabrication of 20 oz copper multilayer PCBs presents significant challenges due to various factors:
Registration: The cumulative tolerance across the 0.7 mm thickness of copper can lead to layer misalignments and difficulties in achieving precise registration.
Aspect Ratios: Plating holes with extremely high aspect ratios, such as 28:1, poses a considerable challenge in maintaining uniform plating throughout the hole.
Lamination Voids: It is crucial to prevent any areas of filler starvation or voids during the bonding process, requiring meticulous precision and control.
Surface Finish: Attaining uniform plating on coarse high copper weight foils is a complex task due to the surface characteristics of the 20 oz copper.
Fine Lines: Defining very fine traces on rough 20 oz foil surfaces presents difficulties in achieving the desired line precision and quality.
Layer Peel Strength: Establishing a very high adhesion level between layers is essential to mitigate the risk of delamination.
Via Filling: Copper plating high aspect ratio holes without any pore formation demands specialized processes to ensure pore-free via filling.
Hole Wall Quality: Smooth and resin-rich hole walls are critical to enable proper copper plating and ensure the integrity of the plated vias.
Drilling: Achieving straight vertical through holes without taper or breakage requires the use of specialized drill bits and rigs.
Panel Stress: Minimizing cumulative stresses, as well as addressing issues like bowing and twisting during fabrication, is crucial to maintain the integrity and reliability of the PCB.
These factors necessitate the utilization of highly mature manufacturing capabilities, stringent controls, and advanced techniques to consistently produce high-quality 20 oz PCB.
Methods for Making 20 Oz PCB
The production of 20 oz PCB presents specific challenges compared to the manufacturing of regular boards. These difficulties primarily involve drilling processes, laminated structures, solder mask printing, and etching accuracy. Currently, three methods are commonly employed in the production of heavy copper PCB:
Electroplating:
Due to the limited availability of thick copper foils in the market, manufacturers typically start with 5 oz copper foils. Higher thickness orders are processed by electroplating to increase the copper thickness. However, this method poses challenges in terms of plating time, electroplating equipment capacity, overall cost and ensuring uniformity in both plating and etching processes.
Lamination:
This method involves laminating one layer of heavy copper foil onto the board. Although this approach offers better uniformity in copper thickness compared to electroplating compared to electroplating, it nevertheless necessitates several etching phases to realize the intended pattern.
Etching:
In this method, etching is performed on both aspects of the copper foil. To commence, a pattern is etched onto one side of the copper foil at half the depth. This etched pattern is then pressed onto the board and furthered along with the regular manufacturing sequence post-lamination. Subsequently, the second aspect of the copper foil undergoes etching in conjunction with the residual copper thickness and the substrate, leaving the initial pattern pressed into the substrate.
These methods, though challenging, are employed to overcome limitations in the availability of thick copper foils. Each approach has its specific considerations, including cost, uniformity, etching accuracy, and the overall production process. Manufacturers carefully evaluate these factors to determine the most suitable method for producing 20 oz PCB.
Applications of 20oz Printed Circuit Boards
A 20oz PCB denotes a printed circuit board characterized by a copper weight of 20 ounces for each square foot (oz/ft²), roughly equating to 6.93 kilograms for each square meter (kg/m²). The weight of the copper indicates the thickness or quantity of copper prevalent on the surface of the PCB.
PCB boasting an elevated copper weight, for instance, 20oz, are typically employed in applications that necessitate superior current carrying capability, low resistance, and effective heat dissipation. Below are several examples of applications that might benefit from the use of a 20oz PCB.
Power Electronics:
In power electronics applications, such as motor drives, power inverters, or high-power amplifiers, where high currents flow through the PCB, a 20oz copper weight can handle substantial power transmission while minimizing resistance and voltage drops.
High-Current Applications:
PCB characterized by 20oz copper are also apt for applications tied to high-current circuits or power distribution, such as charging facilities for electric vehicles (EV), industrial apparatus, or expansive power supply units.
LED Lighting:
LED illumination systems, predominantly those employed in commercial or industrial contexts, frequently demand proficient heat dispersal due to the elevated power levels involved. A 20oz PCB can deliver outstanding thermal conductivity, assisting in dissipating heat produced by the LEDs, thereby extending their operational longevity.
RF/Microwave Applications:
Radio frequency (RF) and microwave circuits often require specific impedance matching and controlled transmission line properties. A 20oz PCB can be used to design RF/microwave components like filters, amplifiers, or antennas that need low-loss characteristics and precise signal integrity.
High-Frequency Applications:
For applications involving high-frequency signals, such as wireless communication systems or radar systems, a 20oz PCB can help maintain signal integrity, reduce signal loss, and minimize impedance variations.
It’s important to note that PCB with higher copper weights are generally more expensive and may require specialized fabrication techniques. The design and manufacturing of such PCB usually involve factors like thicker copper plating, wider traces, and appropriate thermal management considerations.
20 oz Extreme PCB Manufacturer – JarnisTech
When it comes to 20 oz PCB, their heavy copper composition necessitates specialized technologies to ensure optimal outcomes. It is crucial to collaborate with a reputable PCB manufacturer who can deliver high-quality results despite the challenges involved in fabricating such thick copper boards. One such exceptional manufacturer is JarnisTech, with years of experience in this field.
JarnisTech possesses the necessary expertise and knowledge to design and produce top-quality PCB that meet your specific requirements. Our team understands the intricacies of working with 20 oz copper thickness and can leverage our experience to deliver reliable and cost-effective solutions for your printed circuit board needs.
By choosing to work with JarnisTech, you can benefit from our expertise and dedication to delivering superior results in the realm of 20 oz PCB. Trusting their proven experience, you can have confidence in receiving a high-quality PCB design tailored to your precise specifications.
Importance of 20 oz Copper Thickness in Heavy Copper PCB
PCB Circuit Boards are a critical component in electronic devices. They provide the physical infrastructure for arranging electronic components and conductive pathways for electrical signals. The thickness of the copper layers on a PCB plays a significant role in its performance and durability, especially in high-power or high-current applications. A “heavy copper” PCB refers to boards with a copper thickness of 3 oz/ft2 to 20 oz/ft2. Let’s explore the importance of 20 oz copper thickness in heavy copper PCB.
Enhanced Current Carrying Capacity:
The thickness of copper on a PCB directly impacts how much current it can carry without overheating. A PCB fortified with 20 oz copper can accommodate noticeably superior current loads compared to a standard PCB. Therefore, it stands as the perfect selection for applications demanding high power or robust current loads, such as power conversion setups or automobile systems.
Superior Thermal Management:
Heavy copper PCB with a thickness of 20 oz have a greater ability to dissipate heat. This facilitates improved thermal governance, which is imperative for high-powered electronics and systems functioning in elevated temperature conditions. Exceptional thermal governance can enhance the lifespan of the constituent elements as well as the PCB, thereby boosting their resilience.
Increased Mechanical Strength:
PCBs with a copper thickness of 20 oz offer an augmented mechanical robustness. This superior durability proves useful in scenarios where the PCB faces physical strain, characteristic of industrial or automotive operations. The extra copper thickness aids in withstanding potential harm from vibrations, impacts, and various other physical forces.
Improved Reliability:
Enhanced copper thickness equates to increased PCB reliability. Heavy copper PCB are less likely to fail under high stress or high-power conditions, making them ideal for critical applications where failure is not an option.
Cost-Effective for High-Power Applications:
While the cost of manufacturing heavy copper PCB is higher than standard PCB, they can be more cost-effective in the long run for high-power applications. The increased durability, dependability and excellent thermal regulation attributed to heavy copper PCB can curtail maintenance expenditures and prolong the device’s operational life. This contributes to comprehensive cost savings in the long term.
In conclusion, the use of 20 oz copper thickness in heavy copper PCB is crucial in specific applications. It allows for enhanced current carrying capacity, superior thermal management, increased mechanical strength, and improved reliability, making them an ideal choice for high-power, high-stress applications.
Conclusion
As electronic systems strive for greater performance and power densities, the utilization of 20 oz copper PCB with 0.7mm thick copper has emerged as the cutting-edge solution in PCB fabrication. These advanced PCB offer unparalleled capabilities in terms of current capacity, thermal management, and reliability. However, achieving flawless quality and high yield rates necessitates overcoming substantial manufacturing challenges on a large scale.
To mitigate risks and ensure successful implementation of state-of-the-art 20 oz copper PCB technology, it is crucial to establish a partnership with an esteemed PCB company that possesses proven expertise in this highly specialized arena. Selecting an elite PCB company with deep knowledge and experience in manufacturing 20 oz copper PCB is instrumental in overcoming complexities and ensuring optimal results.
Through alignment with a reliable PCB manufacturer, you avail critical support, mentorship, and vital resources, crucial for maneuvering the complexities associated with fabricating 20 oz copper PCB. This strategic partnership minimizes risks, maximizes efficiency, and enhances the overall success of your implementation of leading-edge 20 oz copper PCB technology.