The assembly of Rigid flex PCB amalgamates the merits of both rigid and flexible circuit boards, proposing an exclusive answer for applications that put a premium on factors like space, weight and durability. The incorporation of rigid and flexible substrates clears the way for intricate and dense designs while catering to the requisite adaptability for bending or folding.
Rigid flex PCB assembly has emerged as a crucial technology in modern electronics, enabling compact and flexible designs without compromising reliability. This piece presents a comprehensive guide to the core concepts and functional tenets of rigid-flex PCB assembly, underscoring its importance across myriad sectors.
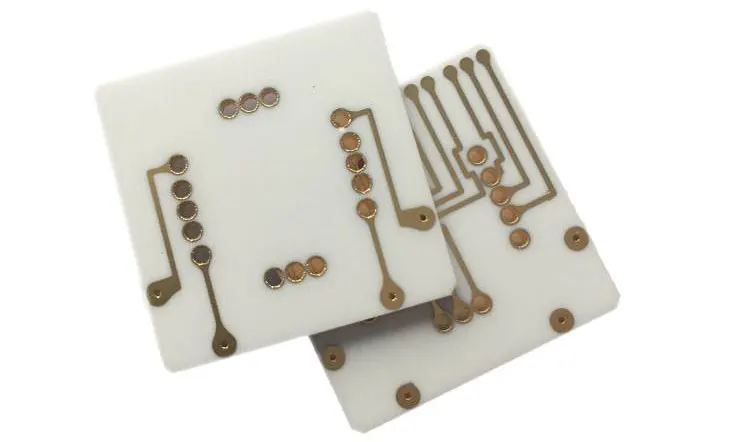
What is a Rigid-Flex PCB?
A Rigid-flex PCB exemplifies a special circuit board that combines the benefits of a rigid and Flexible an interchanging structure of two types of PCB layers. This unique construction provides numerous advantages over traditional PCB, particularly in terms of ease of installation and packaging. Furthermore, rigid-flex PCB extend economic viability, making them exceedingly befitting for high-density applications.
Rigid-flex PCB are notably apt for industrial and commercial utilization where they optimize space efficiency and augment reliability by excluding the requirement for separates wiring and bendable cabling. By integrating the circuits into the overall construction of the PCB, these boards deliver improved electrical performance and enhanced service reliability, making them the preferred choice for high-reliability applications.
Nonetheless, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the design process for rigid-flex PCB can prove to be intricate. Prudence in paying attention to minute details is integral to guarantee the precise placement of each constituent. The alignment of the layers in rigid-flex PCB requires careful consideration, necessitating a thorough design approach. In spite of the additional cost and complexity involved, the multitude of benefits proffered by rigid-flex PCB deem them a meritorious investment.
Overall, rigid-flex PCB provide a professional solution for various applications, offering enhanced reliability, space optimization, and cost-effectiveness. Careful design and attention to detail are necessary to fully harness the benefits of these boards.
How Many Types for Rigid Flex PCB Circuit Boards?
Many types of rigid-flex PCBs exist, every one featuring its distinct structure and practical applications. Here’s a presentation of several prevalent types:
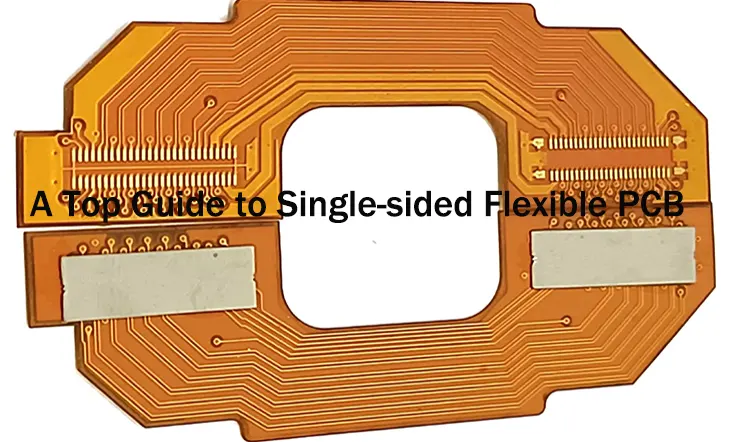
1. Single-sided Rigid-Flex PCB: This types of rigid-flex PCB introduces a single flexible stratum incorporated onto a rigid one. It finds frequent usage in scenarios demanding compact space utilization, typical of petite electronic devices.
2. Double-sided Rigid-Flex PCB: In this type, both sides of the flexible layer are bonded to rigid layers, creating a more robust and versatile circuit board. It accommodates intricate circuit design and is customarily employed in applications necessitating a greater density of components.
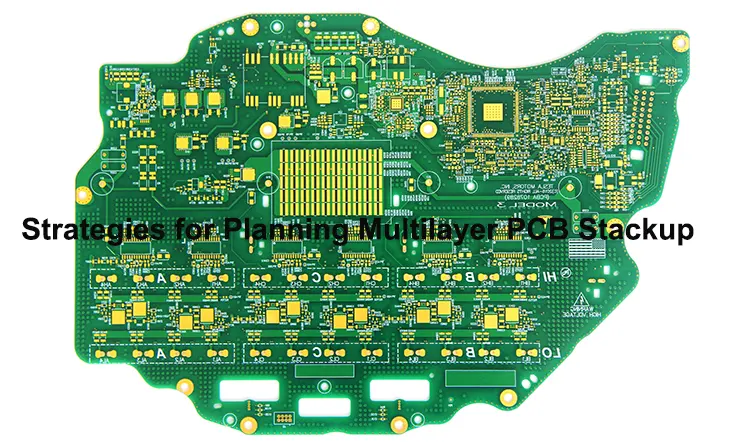
3. Multi layer Rigid-Flex PCB: This type of rigid-flex PCB has multiple layers of flexible material interleaved with rigid layers. It offers amplified design flexibility, accommodating intricate circuit designs and interlinking. Multi-tier Rigid-Flex PCB generally find prominence in high-efficiency and high-reliability application scenarios.
4. Sculptured Rigid-Flex PCB: This category of rigid-flex PCB is characterized by rigid segments interconnected via flexible divisions. The flexible sections can be shaped or contoured to fit specific mechanical requirements. Sculptured rigid-flex PCBs are routinely employed in applications where there’s a requirement for the PCB to conform to a non-linear or unconventionally shaped housing.
5. Dynamic Rigid-Flex PCB: Dynamic rigid-flex PCBs are engineered to maintain their electrical functionalities even with constant bending and flexing. They frequently find applications in scenarios demanding recurrent motion or bending, exemplified by wearable technology or foldable electronic devices.
Each type of rigid-flex PCB has its own advantages and considerations, and the choice depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Step-by-Step Process of Rigid-Flex PCB Assembly
The assembly of rigid-flex PCB is a sophisticated procedure that involves the combination of rigid and flexible circuit boards to create a single integrated assembly. Here is a step-by-step process for rigid-flex PCB assembly:
1. Design and Layout: The initial phase involves designing the rigid and flexible circuit boards employing dedicated PCB design software. The design should take into account the specific requirements of the application and the mechanical limitations of the assembly.
2. Fabrication: Upon finalizing the design, the rigid and flexible circuit boards undergo independent fabrication. This fabrication procedure encompasses processes like copper trace etching, hole drilling, and solder mask and silkscreen application.
3. Component Placement: Once the circuit boards have been manufactured, the subsequent phase involves the accurate place of the various components on both the rigid and flexible boards. This involves using automated pick-and-place machines to accurately position the components according to the design specifications.
4. Soldering: Once the components are accurately placed, the following step entails soldering these onto the circuit boards. This process could be carried out via wave soldering or reflow soldering methods, depending on the specific requirements of the assembly.
5. Testing: Subsequent to soldering, the assembled rigid-flex PCB is subjected to a diverse set of tests to validate its functionality and dependability. These tests encapsulate electrical testing, functional testing, and occasionally, environmental testing to mimic real-world scenarios.
6. Encapsulation: Should it be deemed necessary, the rigid-flex PCB assembly might undergo encapsulation or receive a conformal coating for enhanced protection against elements such as moisture, dust, and various environmental factors. Such a process serves to intensify the longevity and dependability of the assembly.
7. Final Inspection: Prior to the rigid-flex PCB assembly being deemed fit for use, it undergoes a conclusive inspection to verify that all components have been appropriately soldered, to rule out any short circuits or open circuits, and to ascertain that the overall quality is up to the anticipated standards.
8. Packaging and Shipping: Once the rigid-flex PCB assembly successfully clears the final quality check, it gets packaged and readied for delivery either to the customer or forwarded to the subsequent stage in the manufacturing procedure.
Advantages of Rigid Flex PCB Circuit Boards
Rigid-flex circuits offer numerous advantages in terms of reliability, compact size, and low weight, making them an ideal choice for manufacturers facing the challenge of fitting higher-end technology into smaller spaces. A distinct merit of using rigid-flex circuits lies in their adaptability to be accurately customized to suit the destined device, thereby offering a proficient utilization of the available area.
The economic efficiency of rigid-flex circuit production also stands as a significant advantage for manufacturers. Compared to conventional circuit boards, these circuits can be fabricated more economically, marking them as a desirable selection for budget-driven initiatives. . Additionally, rigid-flex circuits provide improved connection reliability, polarity, and flexibility in packaging, further enhancing their appeal.
The elevated reliability factor of rigid-flex circuits stands as another noteworthy merit. With seamless integration capabilities into diverse applications, these circuits promise unwavering functionality over prolonged durations. Their durability and resistance to shock and vibration make them particularly suitable for demanding environments where the risk of physical stress is high.
Furthermore, rigid-flex circuits offer versatility in terms of size and density. Polyimide circuit boards, for example, can accommodate a high density of connection points, facilitating complex and intricate circuit routing. This flexibility in design allows for greater functionality and performance in compact devices.
In a broad sense, the benefits of rigid-flex circuits extend beyond their reliability and compactness. Their cost-efficiency, heightened connectivity reliability, and versatile packaging flexibility assert these circuits as a dependable and efficient answer for an extensive array of applications, specifically those necessitating high-density circuitry and lightweight configurations.
Applications for Rigid Flex circuits
The employability spectrum of rigid-flex circuits is wide, encompassing multiple sectors. Some ubiquitous instances of their application incorporate:
Aerospace and Defense: Rigid-flex circuits are used in aerospace and defense applications where reliability, durability, and space-saving are critical. They are integral to the nervous system of avionic frameworks, tactical telecommunication devices, missile navigation systems and combat vehicles.
Medical Devices: At the interface of flexibility, compact design, and the capability to endure repeated sterility procedures, the application of rigid-flex PCB circuits thrives in the medical equipment landscape. This encompasses devices such as cardiac pacemakers, defibrillators, diagnostic instruments and health tracking wearables.
Consumer Electronics: Rigid-flex PCB circuit boards are omnipresent across a multitude of consumer electronic devices, including smartphones, tablet computers, notebooks and wearable tech. They provide the necessary flexibility and space-saving capabilities for compact and lightweight designs.
Automotive Industry: Rigid-flex circuits find their usage in automotive applications where size limitations and reliability are paramount. Typically, these circuits are strategically integrated into vehicle control systems, infotainment hubs, dashboard clusters, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Industrial Equipment: Industrial-grade equipment such as robots, control infrastructure, and monitoring devices can leverage the durability of rigid-flex PCB circuits, especially their aptitude for withstanding vibratory, shock, and temperature extremes.
IoT Devices: Playing a pivotal role in the Internet of Things ecosystem, rigid-flex circuits undergird a comprehensive range of IoT devices, from smart home appliances to wearable devices, meteorological sensors, and complex industrial monitoring systems.
Telecommunications: In telecommunication gear, including routers, switches, base stations, and network infrastructure hardware, rigid-flex circuits offer the necessary dexterity and compactness for effective signal transmission and space conservation.
Conclusion
The advent of rigid-flex PCB assembly has brought forth a revolution in electronics, enabling the development of compact, lightweight and highly reliable electronic devices. Fusing the benefits of both rigid and flexible substrates paves the way for manufacturers to actualize inventive designs applicable across various applications. Aspiring to harness this cutting-edge technology to its peak, engineers and designers must possess an in-depth understanding of the underlying tenets and functional procedures of rigid-flex PCB assembly.