Rigid-flex and flex PCB designs have gained significant popularity in the electronics industry, offering flexibility and space-saving advantages. Two popular software tools for designing such PCB are KiCad and Altium. This article aims to compare the capabilities and features of KiCad’s rigid-flex design with Altium’s flex PCB design, helping users make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Introduction to PCB Design Software
PCB design software is a computer program that allows engineers and designers to create, edit, and optimize circuit board layouts for electronic devices. By offering functional solutions for schematic capture, component positioning, signal pathway planning, and manufacturing file yield, these software utilities simplify the overall design process. Therefore, PCB design software plays a crucial role in the electronics industry, enabling the development of efficient and reliable circuit boards.
Features of PCB Design Software
1. Schematic Capture: PCB design software allows users to create and edit circuit schematics by placing and connecting electronic components. Schematic symbols are used to represent various components and their electrical connections.
2. Component Libraries: Design software provides access to extensive component libraries that contain pre-designed symbols, footprints, and electrical models. These libraries save time by offering a wide range of components for use in designs.
3. PCB Layout Editor: The layout editor is a core feature of PCB design software. It allows users to place components on the circuit board, define their physical dimensions, and arrange them in an optimal manner. The editor additionally equips users with the necessary utilities for modifying the setup and direction of components.
4. Signal Routing: PCB design software offers tools for routing electrical traces between components on the circuit board. Traces can be manually routed or auto-routed based on design rules and constraints. Advanced software may include features for differential pair routing, high-speed design, and impedance control.
5. Design Rule Checking (DRC): DRC tools ensure that the design meets specific manufacturing and design requirements. They help identify errors or violations in the layout, such as clearance violations, minimum trace widths, and spacing between components.
6.3D Visualization: Many PCB design software programs include a 3D viewer that allows users to visualize the circuit board in three dimensions. This characteristic aids designers in validating component arrangement, inspecting for interferences or clashes, and appraising the the overall form factor of the board.
7. Manufacturing File Generation: PCB design software generates various output files required for manufacturing, including Gerber files, which define the copper layers, solder mask, and silkscreen. Other files may include the Bill of Materials (BOM), assembly drawings, and fabrication files.
Popular PCB Design Software
●Altium Designer
●Cadence Allegro
●Mentor Graphics PADS
●Autodesk Eagle
●KiCad
●OrCAD
Different software programs offer varying levels of functionality, complexity, and cost. The selection of PCB design software is contingent on considerations such as project requirements, user expertise, available budget, and assistance resources accessible.
What do Kicad and Altium Provide?
KiCad and Altium are both popular PCB design software programs, but they differ in terms of features, capabilities, and target user base. Here’s an overview of what each software offers:
KiCad:
1. Open-Source: KiCad operates under an open-source modality, indicating that its use comes without charge and it possesses an extensive community of users and developers participatory in its evolution and user support.
2. Cross-Platform: Cross-Platform: Subscribing to a cross-platform paradigm, KiCad exhibits compatibility with Windows, macOS and Linux, thereby affirming its reach across a wide spectrum of operating system.
3. Schematic Capture: KiCad provides a robust schematic capture tool that allows users to create and edit circuit schematics.
4. PCB Layout: The software provide powerful PCB layout editor that enables users to design and optimize the physical layout of the circuit board.
5. 3D Viewer: KiCad comes equipped with a 3D viewer, empowering users with the capability to render their PCB designs in a three-dimensional perspective.
6. Gerber File Generation: KiCad is equipped with the capability to produce Gerber files, a critical files extensively utilized in the production process of printed circuit boards.
7. Community Support: KiCad boasts of a bustling user community which proffers user assistance, instructive materials, and resources that aid users in grasping the tool and resources for users to learn and troubleshoot.
Altium Designer:
1. Comprehensive Toolset: Altium Designer offers a comprehensive set of tools for schematic capture, PCB layout, and simulation, providing a complete solution for PCB design.
2. Advanced Features: Altium Designer includes advanced features such as signal integrity analysis, differential pair routing, high-speed design capabilities, and embedded system design.
3. Design Rule Checking (DRC): The software includes built-in DRC functionality to ensure that designs meet specific manufacturing and design requirements.
4. Integrated Libraries: Altium Designer provides an extensive library of components and footprints for easy component selection and placement.
5. Collaboration and Documentation: Altium Designer offers features for team collaboration, version control, and detailed documentation, making it suitable for complex design projects.
6. Manufacturing Output: Altium Designer supports the generation of manufacturing files, including Gerber files, BOMs (Bill of Materials), and assembly drawings.
7. Professional Support: Altium provides professional technical support and training resources for its users.
Both KiCad and Altium have their own strengths and are suitable for different user requirements. KiCad is favored among enthusiasts, learners, and smaller-scale endeavors, while Altium Designer is the go-to choice for seasoned engineers and business entities engaged in intricate and high-caliber PCB designs.
Kicad rigid flex
Kicad rigid flex PCB design is often promoted by companies as a cost-effective solution for producing PCB, particularly for prototyping and small production runs. It offers convenience and affordability in the short term. However, it is essential to consider the limitations and drawbacks associated with this design method.
One significant disadvantage of Kicad rigid flex PCB design is the inability to generate Gerber files and directly print the board. To manufacture prototype boards using Kicad flex PCB, it is necessary to engage a professional PCB manufacturer. Fortunately, Kicad rigid flex Arduino shields can be purchased to access all the features available in the paid version of the software.
Another drawback is the time-consuming nature of manufacturing PCB using Kicad flexible PCB. The design process typically takes between two to eight hours, depending on the user’s familiarity with the software. Additionally, uploading the board files to the computer can be a patience-testing process, taking anywhere from fifteen minutes to six hours before they are ready for testing.
Overall, while Kicad rigid flex PCB design offers cost-effectiveness and convenience for prototyping and small-scale production, it is important to be aware of the limitations and potential challenges associated with this approach.
Overview of Altium’s Basic Package
Altium presents new users with a selection of three distinct packages, each carrying varied prices and functionalities. It is important to consider these options when choosing the most suitable package for your needs
The fundamental package, costing $200 annually, enables users to formulate a restrained quantity of boards. It’s important to highlight, however, that there may be no necessity for users to acquire the latest elements incorporated in this package as their designs will persistently be accessible in the provided library.
For an annual fee of $120, users can access all of Altium’s tools and parts. However, this option provides a decreasing amount of content for each board, including the number of parts and files available.
The Professional package, priced at $500 per year, includes over 90 components in the design library. It also allows users to easily adapt each board to different rigid flex PCB thicknesses, such as medium and thick.
The most expensive package, Altium Designer, costs $600 per year. It offers over 600 parts and access to the latest components from Altium. Additionally, Altium Designer provides a fully-featured editor, enabling users to continuously modify designs and layouts if desired.
It’s crucial to meticulously assess each package’s features and associated costs to ascertain the solution that best aligns with your distinct needs.
Flex and Rigid-Flex Design Challenges
Flexible and rigid flex designs provide benefits in terms of saving space enhancing durability and offering flexibility. Yet they also come with design hurdles that require thorough consideration. Below are some challenges encountered in flexible and rigid flex design:
1. Bend Radius: Flexible circuits possess a minimal bend radius, a standard that must be observed to avert harm to the circuitry or elements. Designers must ensure that the bend radius requirements are met and that the circuit can flex without straining or breaking.
2. Component Placement: Components on a flex or rigid-flex circuit need to be placed strategically to ensure they can withstand the bending and flexing. Additional acknowledgment should be accorded to the placement of high-stress zones or regions prone to recurrent flexing.
3. Trace Routing: Routing traces on a flexible circuit requires careful planning to avoid excessive stress on the traces during flexing. Designers must minimize sharp angles, use curved traces, and avoid crossing traces that may cause fatigue or failure.
4. Signal Integrity: Flex and rigid-flex circuits can be susceptible to signal integrity issues such as impedance mismatches, crosstalk, and signal loss. Proper impedance control, controlled impedance traces, and careful signal routing are essential to maintain signal integrity.
5. Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for flex and rigid-flex circuits is crucial. The materials should have good flexibility, durability, and temperature resistance to withstand the intended application. Compatibility between different materials used in the design is also critical.
6. Testing and Assembly: Testing and assembly of flex and rigid-flex circuits can be more challenging compared to traditional rigid PCBs. Specialized equipment and techniques may be required to ensure reliable connections and proper functioning of the flexible circuit.
7. Cost: Flex and rigid-flex designs can be more expensive compared to traditional PCB due to the specialized materials, manufacturing processes, and testing involved. Designers need to balance the benefits of flex and rigid-flex circuits with the associated costs.
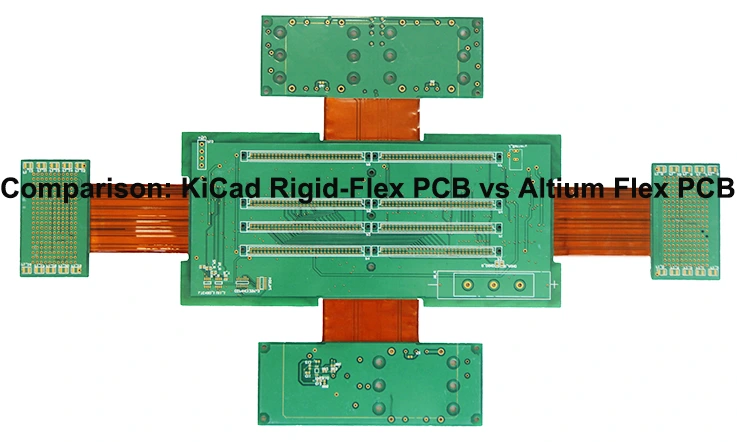
Comparison: KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB vs Altium Flex PCB
Both KiCad and Altium serve as prominent PCB design software extensively utilized within the industry. KiCad presents the facility to design Rigid-Flex PCBs, whereas Altium excels in the domain of Flex PCB design. The following elaborates on a comparative analysis between the two tools:
Design capabilities:
● KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB: KiCad offers limited support for Rigid-Flex PCB. It allows designing boards with multiple rigid and flexible layers, bends, and fold regions.
● Altium Flex PCB: Altium specializes in Flex PCB design and offers advanced features like different stack-ups, bending areas, dynamic flex regions, and length matching for differential pairs.
User interface and ease of use:
● KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB: KiCad has user-friendly interface but may have a steeper learning curve for beginners.
● Altium Flex PCB: Altium has a more intuitive and user-friendly interface, simplifies the initiation process for novices in PCB designing.
Component libraries and footprint creation:
● KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB: KiCad has a wide range of component libraries available, and users can create custom footprints.
● Altium Flex PCB: Altium offers an extensive component library and provides tools for creating custom footprints.
Design rules and constraints:
● KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB: KiCad allows defining design rules and constraints, but it may require more manual work to set up and verify.
● Altium Flex PCB: Altium provides comprehensive design rule checking (DRC) and constraint management tools, making it easier to set up and verify design rules.
Simulation and analysis:
● KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB: KiCad has limited simulation capabilities and does not offer in-house simulation tools.
● Altium Flex PCB: Altium offers advanced simulation and analysis tools, such as signal integrity analysis, power integrity analysis, and thermal analysis.
Collaboration and documentation:
● KiCad Rigid-Flex PCB: KiCad offers collaboration features like version control and allows generating manufacturing files and documentation.
● Altium Flex PCB: Altium provides advanced collaboration features like real-time collaboration, project sharing, and comprehensive documentation generation.
Overall, if you are primarily focusing on Rigid-Flex PCB design, KiCad’s Rigid-Flex PCB option can be a cost-effective choice. However, if you require advanced features, better simulation capabilities, and comprehensive collaboration tools specifically for Flex PCB design, Altium may be a better option.
Creating Rigid-Flex PCB using KiCad: A Step-by-Step Guide
In constructing a circuit via KiCad, there are two main approaches exist – rigid and flexible. Rigid flex PCB offer both rigidity and flexibility, and can be manufactured using standard fabrication processes. On the other hand, flexible PCB provide the flexibility of a wire and are manufactured using selective metal stamping processes with metal powder molds.
Here is a step-by-step guide to creating a circuit using KiCad:
1. Register for a complimentary account and initiate the download of the KiCad software.
2. Kickstart the process by accessing the starter kit file that accompanies your program copy.
3. Download the cost-free KiCad library, encompassing various components and elements pivotal to PCB design.
4. Boot up KiCad and create an untitled, blank project.
5. Customize the hardware for your design by selecting the appropriate board type in the “customize” tab.
6. Employ your new library, components, and parts by navigating to the “library” subsection within the “customize” tab.
7. Begin designing your circuit by placing and connecting components based on your desired functionality. Save your design as you progress.
8. Upon finalizing your design, secure it in the form of a PDF document.
9. Upload the design to a dedicated fabrication site to have your PCB manufactured using high-quality PCB materials. These fabrication sites offer quick turnaround times.
Creating Rigid-Flex PCB using Altium Designer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Altium Designer is a prestigious PCB design software with significant usage within the industry. It serves the requirements of electronics engineers and enthusiasts who are seeking to undertake PCB design undertakings.
Here is a step-by-step guide to creating a PCB using Altium Designer:
1. Begin by downloading the Altium Designer application from the official website.
2. Initiate the software, showcasing an intuitive interface akin to a web browser. Create a new project swiftly within this environment.
3. Customize the board by selecting the appropriate hardware and components that suit your design requirements.
4. Incorporate several components to your circuit, including resistors, capacitors, transistors among others, by leveraging the comprehensive library provided in Altium Designer.
5. Upon accomplishing your circuit design, navigate to the “fabrication” tab. This function allows the generation of the terminal design file imperative for professional-grade PCB production.
6. Review your design meticulously, ensuring accuracy and correctness, before sending it to the fabrication facility of your choosing.
7. Following this, your PCB will be manufactured, and you can anticipate the finalized product’s delivery within a matter of days. The efficiency and user-oriented structure of Altium Designer render it an optimal selection for the creation of flexible PCB, both efficiently and effectively.
Future Trends in PCB Design Software
The future of PCB design software is focused on leveraging the latest technologies, particularly in terms of simplicity and ease of use. Leading companies such as Altium, KiCad, and others are actively working on developing game-changing solutions. One of the key goals is to enable a “one-click PCB” approach, where circuit design can be accomplished with a single click.
These software programs are continually improving their user-friendliness, often with the support of major companies. As this trend forges ahead, it surfaces that forthcoming generations will possess the capacity to architect their own circuits from their residences. Progressions encompass pragmatic 3D circuit simulation, increasingly user-friendly schematic design procedures, and additional characteristics that streamline circuit design tasks.
It’s paramount to note that while these programs offer significant capabilities, they do not eliminate the need for user input. It is crucial to understand the fundamentals of PCB design and utilize these software tools as aids. However, the advancements made in recent years are remarkable, making it increasingly accessible for individuals to design their own PCB circuit boards.
As technological advancements persist, there will be an increasing array of opportunities for circuit board design. The strides made to date are genuinely remarkable. If you harbor intentions to fabricate circuit boards in china in the imminent future, it is recommended to acquaint yourself with these software tools and their corresponding competencies.
Conclusion
Both KiCad and Altium bestow potent tools for engineering rigid-flex and flex PCBs. KiCad presents an open-source, cost-efficient solution backed by an active user community, Altium offers a professional and comprehensive design environment with advanced features. The selection between the two ultimately hinges on the user’s specific necessities and predilections. Irrespective of the software chosen, the escalating popularity surrounding rigid-flex and flex PCB designs underscores their potential for revolutionizing the electronics industry.