Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs are a solid choice for high-power applications, including LED lighting, power supplies, and industrial electronics. These PCBs feature a durable aluminum substrate that significantly improves heat dissipation, paired with a copper layer designed to handle the electrical demands of complex circuits. Designed for high-performance environments, Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs offer advantages such as superior thermal management, mechanical strength, and reliability.
In this article, we will delve into the design considerations, manufacturing processes, and assembly of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, helping you gain a clear understanding of how to leverage them in your next project.
Introduction to Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
When we talk about Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, we’re diving into the heart of high-performance printed circuit boards that tackle the tough demands of modern electronics. These boards are specifically designed to handle high-power applications, where both thermal management and mechanical durability are a must. From LED lighting systems to power electronics in industrial machines, Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs bring remarkable benefits by offering superior heat dissipation and robust strength.
In this section, we’ll explore what Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs are, how they’re built, and why they’re a great choice for high-demand electronics.
What is Through-Hole Aluminum PCB?
A Through-Hole Aluminum PCB is a specific type of printed circuit board (PCB) that uses an aluminum-based substrate as its primary material, rather than the typical fiberglass or resin used in traditional PCBs. The board is made up of three main layers:
1.Aluminum Substrate: The foundation of the PCB, which provides excellent thermal conductivity (a reliable factor in managing heat in high-power applications).
2.Dielectric Material: Positioned between the aluminum base and copper layer, this insulating material helps maintain the PCB’s electrical performance while facilitating heat transfer.
3.Copper Layer: The copper layer is where the actual circuit paths are formed. It’s this layer that connects all the electronic components.
What makes Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs particularly valuable in high-power electronics is their ability to handle intense heat without degrading. In a typical LED lighting system, for instance, the copper layer carries the current to the LED components, while the aluminum substrate takes the excess heat generated and dissipates it efficiently into the environment, preventing any damage to the components.
In applications requiring high thermal conductivity, such as power supplies for industrial machinery or automotive electronics, these boards outperform conventional PCBs by a long shot. The copper layer allows for high current density, while the aluminum substrate ensures that heat doesn’t build up and cause failure.
Why Choose Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs for High-Power Electronics?
In high-power electronics, one of the primary concerns is heat management. Whether you’re dealing with power supplies or LED systems, managing temperature is a constant challenge. Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs excel in this area due to their exceptional thermal conductivity.
The aluminum layer of these PCBs acts like a heat sink, drawing heat away from the components and distributing it across the board. This helps to prevent overheating, which can cause failures or degradation of components over time.
For example, high-power LED lights generate significant heat. Without an efficient way to manage this heat, the LEDs would lose efficiency and burn out faster. By using Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, the heat from the LEDs is effectively spread out, allowing the lights to function longer and more effectively.
These PCBs also feature strong mechanical properties, which makes them a good fit for environments with high levels of vibration or physical stress, such as automotive or industrial machinery applications. They handle physical stresses well and are durable enough to ensure that the system remains intact over time.
Advantages of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs for Industrial Applications
In the world of industrial electronics, products often face extreme conditions. Whether it’s high temperatures, constant vibrations, or heavy-duty power needs, the components need to perform reliably in these environments. Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs are designed to handle these conditions and more.
●Heat Dissipation: In applications like power converters, inverters, or electric motors, excess heat can quickly become an issue. By using Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, the aluminum substrate helps efficiently transfer heat away from sensitive components, allowing the systems to operate at higher power without compromising reliability.
●Strength and Durability: Industrial machinery often experiences harsh conditions, including vibrations, shocks, and rough handling. The robust nature of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs makes them ideal for these kinds of settings. Their mechanical strength ensures that they stay intact even under stressful conditions, so the devices they power can continue operating smoothly.
For example, industrial robots. These machines, designed for tasks such as assembly, material handling, and inspection, require high-powered electronics to function. The PCB in such a robot needs to handle both power requirements and heat without failure. Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs provide the ideal balance of performance and strength to ensure that the robot’s electronics work without issue, even after long hours of continuous operation.
Structural Design of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs

Designing Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs is all about ensuring that the board performs effectively under high-power applications like LED lighting, power electronics, and industrial equipment. The board has to withstand high currents and manage heat dissipation while maintaining a stable connection for all components. A well-structured PCB can make a big difference in how long it lasts and how well it handles thermal stress. In this section, we’ll explore the core elements of PCB design that contribute to their performance and longevity.
Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs are more than just a combination of materials. The layout, the choice of materials, and the specific design techniques all work together to ensure the board handles heat and power without issue. By paying attention to the right design strategies, you can avoid potential failures and get the most out of your high-power circuits.
Structural Design Considerations for Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
When designing Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, the PCB layout and the placement of vias are essential considerations. A well-thought-out design maximizes heat dissipation and ensures electrical stability. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
●PCB Layout: The layout of a PCB will affect how effectively heat is managed. In high-power circuit designs, how components are arranged on the PCB plays a big role in managing heat. Placing power components in close proximity to the substrate ensures that the heat can be quickly transferred away from the components. At the same time, you need to avoid overcrowding the board, as it could make heat dissipation less efficient. Think of it like spacing out the parts in an oven so the heat can circulate effectively.
●Via Design: Vias play a main role in moving heat from the top layers of the PCB down to the aluminum substrate The better the via design, the more effective the heat transfer will be. Special thermal vias should be used to direct heat from the copper traces straight to the aluminum substrate. If the via design is poor, the heat won’t travel efficiently, which could lead to overheating and potential failures. Consider using larger vias or more vias to ensure better heat management.
●Heat Dissipation: To get the best results from your Through-Hole Aluminum PCB, you need to make sure that the heat generated by your components has a way to spread out. This involves more than just the substrate—the copper traces play a role too. Using wider copper traces around high-power components can help spread the heat across the board and prevent localized overheating. Additionally, using multiple layers can also contribute to better heat distribution, as each layer can help manage and move the heat where it needs to go.
The structural design of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs isn’t just about fitting the components together—it’s about ensuring that the heat generated in the process has the right channels to dissipate. When done right, these design choices ensure that the board performs effectively and lasts longer.
Advanced Manufacturing Techniques for Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
Creating Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs isn’t just about combining the right materials—it’s about knowing how to manufacture them with precision. From the initial PCB fabrication process to ensuring thermal management and conducting rigorous quality control, each step plays a role in guaranteeing the PCB’s performance in demanding high-power applications like LED lighting, power electronics, and industrial devices.
In this section, we’ll dive into the manufacturing process, thermal management strategies, and quality control measures that make Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs suitable for high-performance applications. By understanding these techniques, we can ensure our designs deliver the durability and reliability needed for real-world use.
PCB Fabrication Process for Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
Through-Hole Aluminum PCB manufacturing begins with selecting the right materials. The aluminum substrate serves as the foundation, while the dielectric layer and copper layer complete the multi-layered structure. The fabrication process involves several steps:
●Material Selection: The first step in PCB fabrication is choosing the right materials. High-quality aluminum substrates with good thermal conductivity and durability are essential. The dielectric material must be chosen based on its electrical properties to ensure that it provides the necessary insulation while supporting the electrical current flowing through the PCB. Copper plating on the surface allows for smooth, reliable signal transmission.
●Drilling: For Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, the next step is drilling the vias. Vias are holes that connect the copper traces from one layer to another. The accuracy of this step is crucial, as it ensures a proper electrical connection between layers. Drilling too deep or too shallow can affect the PCB’s performance.
●Copper Plating: After drilling, the PCB goes through a copper plating process. This step involves depositing a thin layer of copper on the aluminum substrate, ensuring that electrical signals can flow through the traces effectively. It’s also crucial for the thermal management aspect, as copper is a good conductor of heat.
●Lamination and Etching: Finally, the PCB undergoes lamination, where the layers are fused together under heat and pressure, followed by etching, which creates the necessary copper traces for the electrical paths.
This careful process guarantees that the Through-Hole Aluminum PCB is not only electrically sound but also built to handle the heat and power demands that come with LED systems, power electronics, and other industrial applications.
Thermal Management in the Manufacturing of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
Effective thermal management is core in designing and manufacturing Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, particularly for high-power applications. As power demands rise, controlling temperatures is necessary to maintain the PCB’s proper function and prevent overheating.
Here’s how thermal management is incorporated into the manufacturing process:
●Thermal Pads: Thermal pads are used to facilitate heat transfer from sensitive components to the aluminum substrate. These pads are typically placed between heat-generating components, like LEDs, and the aluminum base, helping to spread heat over a larger surface area. This increases the overall thermal dissipation and lowers the risk of hot spots that could damage the PCB or reduce its lifespan.
●Heat Sinks: In high-power applications, heat sinks are commonly attached to aluminum PCBs to help manage heat. By increasing the surface area that comes into contact with the air, heat sinks allow for more efficient heat transfer. These devices are especially helpful in designs where active cooling isn’t an option, as they provide a way for heat to dissipate over time without requiring additional energy input.
●Copper Layers for Heat Spread: In addition to aluminum, copper plays a core role in thermal management. The copper traces act as heat spreaders, helping move excess heat away from high-temperature areas of the PCB. By designing via connections effectively, heat can be conducted from one layer to another, preventing temperature build-up at critical points.
The inclusion of thermal pads and heat sinks during the manufacturing process ensures that the PCB can handle high-power currents and heat without compromising its performance or reliability.
Quality Control in Through-Hole Aluminum PCB Production
Quality control (QC) during the production of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs ensures that each board meets the necessary standards for use in LED lighting, power electronics, and industrial applications. Every phase of the manufacturing process requires close inspection, as even small imperfections could lead to issues in the board’s performance. Rigorous testing and checks help confirm that the final product performs consistently and reliably.
Main elements of the quality control process include:
●Reliability Testing: After PCB fabrication, each unit undergoes rigorous reliability testing to simulate the stress the board will experience in real-world applications. This could include thermal cycling, where the PCB is exposed to extreme temperature variations, or vibration testing, where the PCB is subjected to vibrations to ensure it can withstand mechanical stress in environments like industrial machinery.
●Visual Inspection and Electrical Testing: Visual inspection is often done using automated optical inspection (AOI) systems to ensure there are no defects in the copper traces, vias, or component placement. Electrical testing follows, where the PCB is powered to verify all connections are intact, and signals are correctly transmitted through the layers.
●Performance Standards Compliance: During production, the Through-Hole Aluminum PCB must meet several performance standards, including electrical and thermal performance specifications. For example, thermal resistance must be within a certain range to ensure heat is dissipated effectively, and the copper traces must have the correct thickness to handle high current without causing resistance issues.
●Endurance Testing: Testing how long the PCB can sustain continuous power is another aspect of quality control. Endurance testing involves running the PCB through extended cycles to ensure that it performs consistently over time, especially when subjected to heat and high currents.
All these quality control measures are designed to confirm that Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs will deliver consistent, reliable performance across all types of applications, whether it’s an LED circuit or industrial-grade electronics.
Design Considerations for Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs

Designing Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs requires careful attention to a variety of factors that influence the overall performance of the PCB, especially in applications that demand high power handling. The PCB layout, heat dissipation, and the integration of components such as heat sinks and thermal pads all contribute to ensuring that the PCB operates efficiently, even in demanding environments like LED lighting, power electronics, and automotive electronics.
Optimizing Through-Hole Aluminum PCB Layout
The layout of a Through-Hole Aluminum PCB impacts both electrical performance and heat management. When designing the PCB, it’s necessary to consider factors like current handling, thermal paths, and component placement. Below are strategies for optimizing the Through-Hole Aluminum PCB layout to ensure reliable performance:
| Layout Element | Design Strategy | Purpose |
| Via Placement | Position vias near heat-sensitive components. | Enhance heat dissipation by improving the thermal path. |
| Trace Width Calculation | Use wider traces for paths carrying high currents. | Minimize voltage drops and mitigate the risk of overheating. |
| Component Distribution | Distribute components to avoid placing heat-sensitive ones near high-power parts. | Ensure efficient cooling by reducing thermal stress. |
| Ground Plane Design | Implement continuous ground planes to support current flow and heat dissipation. | Help ensure stable signal integrity and assist with heat management. |
With these design techniques in place, the Through-Hole Aluminum PCB can perform more effectively, particularly in high-power applications where thermal management is a primary concern.
High-Power PCB Design: Managing Heat and Current
Managing heat and current effectively is essential when designing high-power PCBs. The combination of high current density and heat generation can lead to circuit failure if not addressed properly. Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs help by utilizing aluminum substrates, which offer high thermal conductivity, aiding in heat transfer away from critical components.
| Design Technique | Description | Benefit |
| Thermal Via Design | Include via holes to help dissipate heat from high-temperature regions to the back layer. | Enhance thermal conductivity and optimize heat dissipation. |
| Current Density Management | Design traces to handle high current by using wider paths for high-power components. | Prevent overheating and maintain stable electrical performance. |
| Power Distribution Networks | Optimize power distribution to minimize voltage drops and ensure stable current supply. | Maintain a consistent current flow and reduce potential damage to components. |
Proper heat and current management is a fundamental part of designing high-power PCBs. Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs provide an effective structure for managing the flow of electricity while addressing the thermal challenges that arise from high-power use.
Integrating Heat Sinks and Thermal Pads in Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
When designing high-power electronics, it’s often necessary to integrate heat sinks and thermal pads into the Through-Hole Aluminum PCB to improve heat management. These components help direct heat away from the PCB, reducing the risk of overheating and improving the overall performance of the system.
| Component | Description | Effectiveness |
| Heat Sinks | Attach heat sinks to PCBs close to high-power components to increase surface area. | Assist with passive cooling by spreading heat more evenly. |
| Thermal Pads | Position thermal pads between heat-sensitive components and the aluminum substrate. | Improve thermal conductivity and assist with heat transfer. |
| Thermal Vias | Implement thermal vias to transfer heat from the top layer to the aluminum substrate. | Speed up heat dissipation and help maintain a consistent temperature. |
By integrating these components effectively, Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs can dissipate heat efficiently, improving the overall performance of high-power electronics.
Challenges and Solutions in Through-Hole Aluminum PCB Assembly
Through-hole assembly in aluminum PCBs presents unique challenges that can affect the overall quality and efficiency of manufacturing. These challenges arise primarily due to the physical properties of aluminum, such as its hardness and thermal conductivity, as well as the precision required for handling through-hole components. In this section, we’ll explore the common issues faced during the through-hole aluminum PCB assembly process and the effective strategies that can help overcome them.
Drill Hole Alignment
●Challenge: Drilling holes in aluminum poses a challenge compared to traditional PCB materials. Aluminum’s hardness and superior thermal conductivity can cause potential misalignment of the drilled holes, impacting the precision required for through-hole component placement.
●Solution: To address misalignment, it’s essential to use advanced drilling equipment with precision controls. . For example, automated optical alignment systems or alignment jigs can ensure that holes align perfectly with component leads. This technology minimizes misalignment and guarantees a smooth manufacturing process.
| Challenge | Solution | Result |
| Misaligned holes | Automated optical alignment & precision drilling | Improved alignment, reduced assembly errors |
| Hard aluminum substrate | Use advanced drilling machines with high torque | Clean holes, reducing misalignment risks |
Soldering Temperature
●Challenge: Due to aluminum’s high thermal conductivity, heat dissipation during soldering becomes more rapid than with conventional PCBs. This can make it difficult to achieve optimal solder joint formation as the heat is lost too quickly during the soldering process.
●Solution: To deal with heat dissipation, we can employ localized heating methods like preheating stations or selective soldering machines. Additionally, implementing temperature profiling during the soldering process ensures that the temperature is controlled throughout the cycle, allowing for uniform heat transfer and stable solder joints.
| Challenge | Solution | Result |
| Heat loss during soldering | Use of preheating & selective soldering machines | Enhanced solder joint formation, stable heat distribution |
| Rapid heat dissipation | Implement temperature profiling | Controlled heat transfer, improving joint quality |
Component Compatibility
●Challenge: Some through-hole components, especially those with plastic or epoxy bodies, may not withstand the higher temperatures required for soldering on aluminum PCBs, which can lead to component failure or degradation.
●Solution: To ensure long-term functionality, it’s need to choose components that are temperature resistant. For example, ceramic packages or high-temperature plastic components can be selected, as these materials can tolerate the increased temperatures associated with aluminum PCB assembly without compromising performance.
| Challenge | Solution | Result |
| Temperature-sensitive components | Use temperature-resistant components like ceramics | Better durability, reduced component damage during assembly |
| Plastic body components | Opt for ceramic or high-temperature plastic alternatives | Stable component performance, no degradation |
Oxide Layer and Solderability
●Challenge: Aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer on its surface, which can hinder solder wetting and the formation of reliable solder joints. This is a common challenge in the assembly of through-hole aluminum PCBs.
●Solution: To address this, proper surface preparation and cleaning techniques must be implemented to remove the oxide layer. Additionally, using fluxes designed specifically for aluminum can help enhance the solder wetting process, ensuring that solder joints are strong and reliable.
| Challenge | Solution | Result |
| Oxide layer formation | Surface preparation & specialized fluxes | Improved solder joint formation, stronger connections |
| Solder wetting issues | Use of aluminum-specific fluxes | Higher-quality solder joints, ensuring electrical reliability |
Mechanical Stress
●Challenge: The rigidity of aluminum PCBs compared to more flexible PCB materials can result in mechanical stress during assembly. This stress can cause solder joint or PCB damage, especially when handling large components.
●Solution: To minimize mechanical stress, design the PCBs with appropriate relief cuts or stress-relieving techniques such as V-scoring or slots. These methods allow for controlled bending, reducing the likelihood of PCB damage during handling. Additionally, selecting components with appropriate lead stiffness ensures that the PCB remains intact during the assembly process.
| Challenge | Solution | Result |
| Mechanical stress during assembly | Use relief cuts, V-scoring, or slots in PCB design | Minimized risk of damage, improved assembly process |
| Stiffness of component leads | Choose components with appropriately flexible leads | Reduced stress on the PCB, better handling stability |
Manufacturing Expertise and Equipment
●Challenge: Assembling through-hole aluminum PCBs requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Precision drilling machines, high-temperature soldering stations, and expertise in handling the unique properties of aluminum are necessary for a successful manufacturing process.
●Solution: Working with experienced PCB manufacturers (JarnisTech) and assembly partners who specialize in aluminum PCB assembly is essential. We have the right tools and expertise to handle aluminum’s thermal properties and rigidity during the through-hole assembly process.
| Challenge | Solution | Result |
| Specialized knowledge and equipment | Collaborate with experienced manufacturers | Better quality, reliable assembly process |
| Handling aluminum’s unique properties | Use advanced tools designed for aluminum PCBs | Enhanced assembly reliability and performance |
Through-Hole Aluminum PCB Vs. Other High-Performance PCBs
In the world of high-performance PCBs, materials are the foundation of a circuit board’s reliability, thermal management, and electrical performance. While Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs are widely recognized for their heat dissipation and strength in demanding applications, they stand in competition with various other high-performance PCB materials, such as Rogers PCB, Taconic PCB, and Panasonic PCB. Here’s an analysis of how Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs compare to these other options, highlighting their unique advantages.
1. Thermal Conductivity:
One of the primary benefits of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs is their superior thermal conductivity. Aluminum itself is an excellent heat conductor, offering thermal performance up to 200 W/m·K, significantly better than materials like FR4, which typically range around 0.3 W/m·K. This makes aluminum a top contender for managing heat in high-power electronics, such as LED lighting and power supplies.
●Rogers PCB: Compared to Through-Hole Aluminum, Rogers’ high-frequency laminates, such as RO4000 and RO3000 series, provide excellent thermal management but are primarily designed for microwave and RF applications. They are not as effective in managing large amounts of heat generated by power electronics.
●Taconic PCB: Taconic offers PTFE-based materials with good thermal properties, but they do not have the same thermal conductivity capabilities as aluminum. While Taconic materials like TSM and TLY can handle certain high-frequency applications, they may not match the aluminum substrate’s heat dissipation ability in high-power applications.
2. Mechanical Strength and Durability:
Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs are known for their durability. The aluminum substrate provides structural integrity and strength, especially in applications requiring mechanical robustness and resistance to vibrations. This is a distinct advantage over other PCB materials like FR4, which, although inexpensive, lacks the durability necessary for heavy-duty environments.
●Panasonic PCB: Panasonic offers a range of materials for industrial and automotive applications, but they are typically based on reinforced epoxy resins. While these materials provide strong mechanical properties, they do not match the rigidity and heat resistance of aluminum when exposed to high temperatures or mechanical stress.
●Isola PCB: Isola’s high-performance materials, such as IS410 and I-Tera MT, are known for their high dielectric properties and high thermal performance in certain conditions. However, they are not specifically designed for the heavy heat dissipation requirements of high-power electronics and therefore are less suitable than Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs in thermal management scenarios.
3. Cost vs. Performance:
While aluminum substrates might have a slightly higher upfront cost compared to standard FR4, they can save you big in the long run. Especially in high-power applications where heat management is a big concern, the aluminum base cuts down on the need for extra heat sinks. The aluminum base reduces the need for additional heat sinks, making it an economically sound choice for high-power applications.
●Nelco PCB: Nelco’s N4000-13 product line offers high-performance PCB laminates for high-frequency and high-temperature environments but at a higher cost. While these materials are suited for extreme environments, they do not offer the same cost-effective heat management as aluminum substrates.
●Tuc PCB: Tuc PCB, specializing in standard FR4 and high-frequency PCBs, provides competitive prices but doesn’t offer the same level of heat dissipation and mechanical strength that Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs provide. In applications like power electronics, the overall performance may suffer from heat-related failures unless external cooling is added.
4. Solderability and Assembly:
Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs have their challenges, particularly in soldering due to the oxide layer on aluminum. However, with advanced surface preparation and specialized fluxes, the solderability of aluminum PCBs can be optimized. This requires attention to detail during assembly but allows for effective manufacturing in power electronics.
●Dupont PCB: Dupont offers advanced materials like Pyralux, known for its flexibility and high-temperature resistance. These materials are excellent for flexible PCBs but are less effective in through-hole assembly for high-power applications compared to aluminum substrates.
●Arlon PCB: Arlon’s substrates, such as AD300C and AD350A, provide robust thermal properties, but again, they are more suited for high-frequency applications and are not as effective in handling through-hole components with high current or heat dissipation needs.
Why Choose Us?
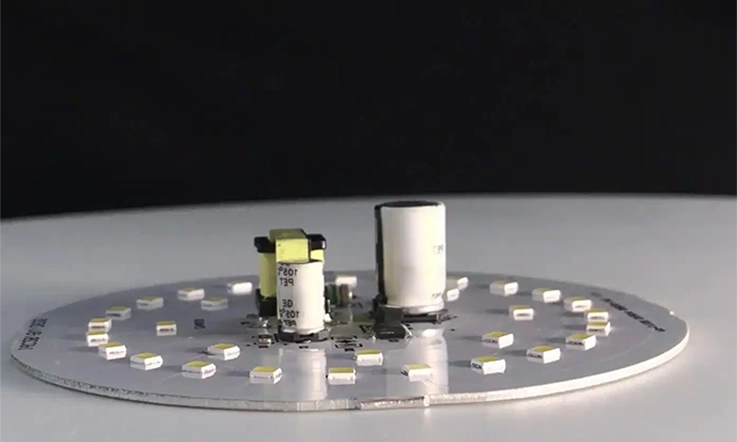
When it comes to manufacturing Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs, experience, precision, and reliability are the key factors that set leading suppliers apart from the competition. We specialize in delivering high-performance aluminum PCBs designed to meet the demanding needs of industries such as LED lighting, automotive, telecommunications, and power electronics. Whether you need custom designs, rapid prototyping, or large-scale production, we bring a wealth of expertise to each project.
China’s Top Through-Hole Aluminum PCB Manufacturer and Supplier
At the forefront of PCB innovation, we have built a reputation as one of China’s top manufacturers and suppliers of Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs. With years of experience and cutting-edge technology, we have successfully partnered with global brands to deliver products that perform consistently in the most demanding applications. Here’s what sets us apart:
1.Expertise in Through-Hole Aluminum PCB Manufacturing-
We offer a comprehensive range of Through-Hole Aluminum PCB solutions, meticulously designed for applications where heat management and mechanical strength are non-negotiable. Our aluminum PCBs are engineered for a wide array of high-power electronics, including LED modules, industrial equipment, and power supplies. With precision fabrication techniques, we ensure each product meets industry standards while providing optimal electrical performance and durability.
2.Industry-Leading Thermal Management Solutions-
One of the standout features of our Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs is their superior thermal conductivity, which outpaces most other PCB materials. By utilizing high-grade aluminum substrates, we maximize heat dissipation, ensuring your high-power devices can handle the toughest operating conditions. This thermal efficiency is crucial in applications such as LED lighting systems, where heat management can directly impact performance and longevity.
3.Customization to Meet Unique Requirements-
Understanding that each project is unique, we provide fully customized solutions. Whether you’re working on a large-scale project or a small prototype, we are equipped to handle orders of any size. From designing the ideal PCB layout for your circuit to selecting the appropriate dielectric material and copper layer thickness, our team works closely with clients to ensure that all specific needs are met. Our flexibility in production allows us to accommodate special requests, such as bespoke thermal pad placements, reinforced copper layers, or custom via designs.
4.Precision Manufacturing with Cutting-Edge Equipment-
We utilize state-of-the-art manufacturing equipment that allows for unparalleled precision in drilling, plating, and assembly. Our advanced drilling technology ensures perfect alignment for through-holes, even when working with hard aluminum substrates. Additionally, our high-precision soldering techniques guarantee reliable component placement, minimizing defects and ensuring maximum longevity for your PCBs.
5.Global Reach with Local Expertise-
While we are based in China, our reach extends worldwide. We have built strong relationships with clients across North America, Europe, and Asia. Our manufacturing facility adheres to international quality standards, and we’re proud to be recognized by top-tier companies across various sectors for the consistency and reliability of our products. We’ve become a trusted partner for businesses looking for top-tier Through-Hole Aluminum PCB solutions, thanks to our ability to deliver cost-effective, high-quality products without sacrificing performance.
6.Speed and Efficiency in Production-
We know that meeting production deadlines is a big deal. Our streamlined production process ensures quick turnaround times without compromising quality. With our automated systems for order tracking and inventory management, we can scale up production quickly while maintaining precision and quality control throughout the entire process.
7.Cost-Effectiveness without Compromise-
We believe in offering competitive pricing without compromising on quality. By leveraging our manufacturing efficiency and long-standing relationships with suppliers, we are able to offer some of the most competitive prices in the industry. Whether you’re ordering in bulk or requesting a small batch, we ensure that your costs remain as low as possible without sacrificing the performance of your Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs.
FAQs about Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs
1.Can Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs be used for RF applications?
Yes, but signal integrity needs careful management.
2.Are Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs suitable for outdoor use?
Yes, with proper conformal coatings.
3.Can Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs be custom-designed?
Yes, they can be tailored to specific needs.
4.How is thermal management handled in Through-Hole Aluminum PCBs?
Using thermal pads, heat sinks, and good PCB layout.
5.What’s the typical thickness of the aluminum substrate?
Typically ranges from 0.2mm to 2.0mm.