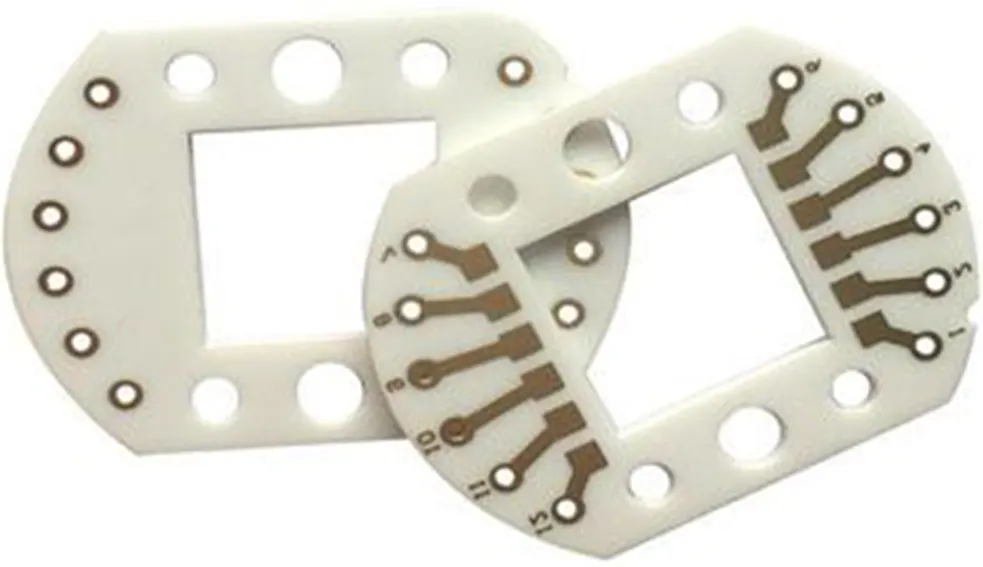
In the manufacturing of circuit boards various base materials are employed and aluminum is favored for ceramic PCB because of its efficient thermal conductivity. Aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Aluminum nitride (AlN) are frequently utilized materials in the production of ceramic PCB. This article will center on ceramic PCB emphasizing their traits and importance, in the PCB industry.
What Is Alumina Oxide Ceramic PCB?
Alumina PCB, also known as Al2O3 PCB is a printed circuit board made from ceramic base material. It has properties like a low thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) and high thermal conductivity. Additionally the purity of Alumina composed of isomorphic crystals exceeds that of other material by a significant margin. Therefore, standout feature of this PCB of type is its thermal conductivity is ranges from 15 to 50 W/mK.
Al2O3 PCB is suite for a diverse array of applications encompassing LED boards as well as high frequency devices. These PCB employ ceramic material and are frequently engineered with multi-layer packaging to augment their functionality. Over the years, Alumina PCB have been subjected to numerous testing stages and have adapted to meet the shifting demands of the industry.
Alumina, when utilized as an engineering material, exhibits exceptional mechanical and electrical attributes. It is among the most prevalent ceramic materials, given its wide spectrum of uses across numerous industries. Alumina PCB usually incorporate a considerable proportion of Al2O3. The superior thermal stability of Alumina boards can boost the efficiency and thermal performance of circuits deployed in automotive applications.
Alumina PCB is available in levels of purity including 96%, 99.5% and the highest at 99.6%. The highest purity level results in a refined surface and a better appearance. Additionally these PCB provide electrical protection and the biocompatibility of Alumina as a ceramic material makes it ideal for medical uses. The unique properties of Alumina PCB enhance performance making them a favored option, across industries.
Alumina PCB Types
The Alumina PCB comprises three different types, they are 96% Alumina Oxide substrate, 99.5% Alumina substrate and 99.6% Alumina substrate. Each types provide unparalleled efficiency in the fabrication of diverse device across a multitude of application.
96% Alumina PCB Substrate:
The 96% Alumina PCB substrate has gained widespread popularity and is now a commonly used substrate material in various microelectronics applications. Thick film substrates are the standard format used in these applications.
The 96% Alumina substrate is extensively used in building hybrid circuits composed of microelectronics, owing to its availability in small dimensions and high tech grade. It is an optimal choice for hybrid devices. Additionally, the 96% Alumina substrate boasts excellent electrical insulation properties, mechanical strength, good thermal conductivity, chemical resistance and dimensional stability.
99.5% Alumina Substrate:
The 99.5% Alumina substrate, which has a smaller grain size, it is ideal for various applications where intricacy is not a crucial factor. However, the Alumina PCB may not be necessary for all application.
The 99.5% Alumina base, known for its larger grain size can reach a top surface smoothness of 2 micro inches. Nevertheless this base demonstrates reduced durability, heat conductivity, electrical insulating capacity and uniformity compared to alternative Alumina bases.
Nevertheless, one of the advantages of the 99.5% Alumina substrate is its availability in larger sizes and superior thickness, which makes it useful for certain applications.
99.6% Alumina Substrate:
The 99.6% Alumina substrate is ideal for creating standardized thin-film substrates and is recommended for in-circuit generation using sputtered, evaporated, and chemically vaporized metals. Its exceptional purity level and smaller grain size enables it to produce smoother results with minimal surface imperfections.
Additionally, the 99.6% Alumina substrate features a surface roughness below 1 micro-inch, which denotes its superior mechanical performance. It also offers low thermal conductivity, exceptional electrical insulation, excellent dielectric properties and corrosion resistance, culminating in outstanding wear resistance.
Why Choose Us?
We stick to a production timetable to ensure on time delivery of our products. Our Quality Control Management System, certified under ISO9001;2015 ensures that all products meet standards upon delivery. We offer a range of ceramic materials designed for various uses. We don’t have any minimum order quantity requirements, so both prototypes and bulk orders will be of high quality.
Our team of experts ensures that we respond to all queries and concerns within 24 hours. With over twenty years of experience in producing and researching ceramics we are dedicated to providing exceptional products and services. Our items have been distributed to over 40 countries earning a reputation, for consistently delivering top notch products on time.
Alumina 2-Layer PCB Stacks Up

Al2o3 Ceramic PCB Manufacturing
The fabrication of Al2O3 PCBs is a sophisticated procedure necessitating utmost accuracy and specialized equipment. This process initiates with the selection of the Alumina substrate, offered in a range of dimensions and thicknesses. Subsequently, the Alumina substrate undergoes a thorough cleaning and pre-treatment phase to guarantee its purity from any contaminants.
●Once the substrate is ready the circuit design is put on it using screen printing. This step includes putting the conductive paste on its surface through a fine mesh sieve to form the required design. The conductive inks utilized are a mix of various metals like gold, copper or silver which serve as efficient conductor, for transmitting signals and power across the circuit board.
●After that the design, on the board goes through a heating process. Here the ink reacts to the heat making the metal particles merge and form a link. This transformation creates a connection that can withstand wear, rust and sudden temperature changes. The outcome is a circuit that offers great performance and longevity.
●After creating the circuit on the board the next important task is to apply the surface finish. This step is vital in production as it shields against rust and boosts the longevity of the board. Immersion gold stands out as a choice for coating Alumina PCB due to its excellent soldering properties, resistance to corrosion and overall reliability, in the long run.
● Afterward the circuit board goes through a quality check to confirm its adherence, to the designated criteria and guidelines. This examination involves an evaluation of different facets. By following this quality control procedure the circuit board is guaranteed to meet the necessary standards of efficiency and dependability.
Properties of Al2o3 PCB
● Conductivity of Low Thermal: The thermal conductivity of alumina PCB typically falls within the range of 15 ~ 50W/mK. In situations where heat is generated by IC or LED, the high thermal conductivity of the alumina material facilitates fast and efficient heat transfer to the PCB. The absence of insulating layer requirement in an alumina based board is attributed to the material’s excellent thermal conductivity.
● High Melting Point: The melting point of alumina substrate varies depending on the purity of the material. Like 96% alumina substrate melts, at 1400oC while a 99% pure alumina substrate has melting point of 1600oC.
● High Strength and Electrical Insulation: Alumina printed circuit boards are highly desirable due to their exceptional electrical insulation properties, rendering them a preferred choice for high-performance applications. The determination of the PCB size can be accomplished by conducting reflectivity reference thickness tests.
● The Lower CET: In ceramic PCB is typically comparable to that of components. In the case of ceramic PCB, the CTE value typically falls within the range of 6 to 8 ppm/oC. This characteristic offer the advantage of reducing stress on solder joints. The lower CTE of the material plays a crucial role in mitigating the risk of component damage resulting from temperature variations.
The important of Alumina PCB In Circuit Board Industries
Alumina hold a pivotal role as a vital material in the manufacturing of printed circuit board, showcasing distinctive attributes that distinguish it from other metals. PCB made of ceramic parts, specifically those composed of Alumina, differ greatly from those made of other material.
Alumina PCBs play a role in the PCB industry especially when other types of PCBs lack the required functionality. The natural strength and robust of Alumina PCBs offer support to electronic components making them ideal, for surface mounting on PCBs. These boards demonstrate performance qualities compared to alternative materials often used in similar scenarios. Although it can be more costly than other materials, this is mainly the case when it is used in the production of the most expensive equipment.
Distinguishing itself from other types of PCB, Alumina PCB do not necessitate a dielectric layer between the circuit and core, rendering them inherently more robust. Irrespective of the chosen manufacturing method, Alumina PCB undergo a multifaceted production process that involves exposure to elevated temperatures.
The production of ceramic PCB involves many stages, with direct copper connecting being a crucial factor. A ceramic circuit board is a solid thermal dielectric material made using both thick-film printing and film printing processes. The surface finish applied to Alumina ceramic PCB is of the utmost importance, with immersion gold being an excellent example of the finish used.
In the manufacturing, directly plated copper is extensively used, The utilization of direct plating techniques for copper deposition holds significant importance and serves as key factor in determining the quality of the final Alumina Ceramic PCB.
Benefits of Alumina Ceramic PCB
● Excellent electrical insulation
● High thermal conductivity
● Resistance to chemical hazards
● Hermeticity
● Versatility
● Cost-effective
JarnisTech provide a range of Aluminum Oxide PCB in different purity levels. Like Al2O3 96%, 99.5% and 99.6%. Our product lineup includes options for film processes with silver metalization and Direct Plated Copper technologies giving customers the ability to select between copper tracks and pad configurations. We are dedicated, to offering solutions that meet the varied needs of our clients.
Common Uses Made of the Alumina PCB
Alumina PCB are commonly utilized in a range of high-performance electronic applications, including:
● Cooling and heating units
● Medical circuits
● LED board sensors
● High-frequency devices
● Aerospace and defense applications
● Automotive electronics
Comparison with Other PCB Substrates
When evaluating the contrast, between Aluminum Oxide PCB and other PCB substrate varieties there are typical attributes that are usually compared:
FR4 PCB
● FR4 is a type of epoxy laminate material widely used for PCB.
● FR4 PCB are cheaper and more commonly used than ceramic PCB.
● FR4 PCB have lower thermal conductivity and may not work as well with high-powered applications.
Metal core PCB
● Metal core PCB use metal (usually aluminum) core with a dielectric layer and a copper layer.
● Metal core PCB have better thermal conductivity than FR4 PCB, but it still not as good as ceramic PCB.
● Metal core PCB are better suited than FR4 PCB for high powered applications.
● Ceramic PCB excel in conductivity allowing them to handle demanding high power operations and effectively disperse heat.
● Ceramic PCB are more expensive than FR4 PCBs and metal core PCB.
● Ceramic PCB have better electrical insulation properties that metal core PCB, which prove advantageous in certain application, especially those involving high voltage requirement.
It’s crucial to highlight that when comparing these kinds of PCB materials it greatly depends on the particular needs of the application at hand. This includes aspects, like power needs how well they handle heat, operating frequency, size limits, cost factors and overall dependability.
Alumina Prototype Ceramic PCB Delivery Date and Price
The cost of Alumina PCB can fluctuate based on various factors encompassing board dimensions, order volumes, and unique manufacturing specifications. To facilitate the quotation process, customers are encouraged to furnish us with Gerber documents that comprehensively outline their specific requirements.
At JarnisTech we usually deliver FR4 and aluminum PCBs within 5 – 7 days. Alumina Ceramic PCBs take longer to make due to their complex manufacturing process. They typically require, around 13 15 days to complete. However we understand the importance of meeting our customers urgent requirements. That’s why we offer expedited order choices that in situations can be processed within a week for prompt delivery.
Future Developments and Prospects of Alumina Ceramics PCBs
Increased integration: Alumina ceramic PCB are well-suited for more integrated designs, where compact size and higher levels of integration are essential.
Advanced materials: like silicon carbide (SiC) or boron carbide (B4C) can be mixed with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) to boost heat conduction enhance durability or cut down on expenses.
Functionalization: Alumina ceramic circuit board can be personalized to incorporate functionalities like sensing, actuation or energy harvesting through the integration of supplementary materials and devices, onto their surface.
Printing technology: Utilizing additive manufacturing methods such, as 3D printing enables the production of intricate and personalized ceramic PCB leading to enhanced performance and shorter production lead times.
Environmental technology: Alumina ceramic PCB offer an alternative to conventional PCB potentially driving up the demand for ceramic PCB due, to growing environmental awareness.
Final Thoughts
This article offers a look at Alumina Ceramic PCB discussing their distinct features, benefits, drawbacks and possible uses. It’s worth mentioning that Alumina PCB have become a choice for high performance power applications serving as a valuable addition, to the electronics industry compared to traditional aluminum and copper based PCB.
If you’re looking for notch ceramic printed circuit board and assembly services feel free to contact JarnisTech. Our team specializes in crafting high precision Alumina PCBs. Provides outstanding assembly services tailored to meet our clients diverse needs.
Related Posts:
●Overview of Alumina Substrate
●How Layout a Multilayer Ceramic PCB Stack-ups?
●How to Design a Ceramic Circuit Board?
●Leading Global 12 Ceramic PCB Manufacturers
●Manufacturing Standards for Ceramic PCB Production
●What is Ceramic Packages and Its Types?
PCB Fabrication
Ceramic PCB Manufacturing & Assembly